White solder mask is a popular choice for metal-core LED PCBs, offering both optical and thermal advantages. When designing circuit boards for LED applications, engineers must balance two critical factors:
- Optimal Light Reflection – White solder mask enhances brightness by improving light diffusion, ensuring clean and accurate color rendering from LEDs.
- Efficient Heat Dissipation – Since LED components generate significant heat, the reflective properties of white solder mask help manage thermal performance, especially when paired with metal-core substrates.
By improving both light output and heat management, white solder mask has become a key material in high-performance LED PCB designs.
Introduction
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the unsung heroes of our electronic devices, providing the foundation upon which all components are mounted and interconnected. For decades, the iconic green color has been synonymous with PCBs. However, as technology advances and design aesthetics evolve, white PCBs are emerging as a popular alternative, offering both functional and visual benefits.
What is a White PCB?
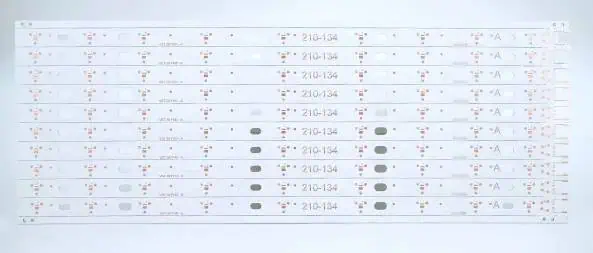
1 Definition and Composition
A white PCB, at its core, is similar to any other PCB in terms of its basic structure and function. The key difference lies in the color of the solder mask – the protective layer applied to the copper traces of the PCB. In white PCBs, this solder mask is, as the name suggests, white instead of the traditional green.
2 Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for white PCBs is largely similar to that of traditional PCBs. The primary difference occurs during the application of the solder mask. White solder mask is typically made from epoxy-based materials with added pigments to achieve the desired color and opacity.
Read more about:
Advantages of White Circuit Boards
White PCBs offer several advantages over their green counterparts, making them increasingly popular in various applications.
1 Enhanced Visibility
One of the most significant benefits of white PCBs is improved visibility. The white background provides a stark contrast to component markings, solder joints, and copper traces, making it easier for engineers and technicians to inspect, assemble, and troubleshoot boards.
2 Heat Reflection
White surfaces naturally reflect more light than darker colors. This property translates to better heat reflection in white PCBs, potentially leading to improved thermal management in electronic devices.
3 Aesthetic Appeal
In an age where design aesthetics are increasingly important, white PCBs offer a clean, modern look. This is particularly valuable in consumer electronics where the PCB might be visible, such as in transparent or translucent device casings.
4 Customization Opportunities
The white background of these PCBs provides an excellent canvas for custom designs, logos, or additional information to be printed directly on the board, enhancing branding opportunities.
Top Brands of White Solder Mask
Several manufacturers have developed high-quality white solder mask products to meet the growing demand. Some of the leading brands include:
1 Taiyo
Taiyo is renowned for its PSR-4000 AUS308 series, which offers excellent whiteness and stability.
2 Peters
Peters’ SD 2950 series is known for its high-performance white solder mask suitable for a wide range of applications.
3 Huntsman
Huntsman’s Probimer series includes white solder mask options that provide excellent coverage and durability.
4 Electra Polymers
Electra Polymers offers the EMP110 series, which includes high-quality white solder mask options.
Applications of White PCBs

White PCBs are finding their way into various applications across multiple industries.
1 LED Lighting
In LED applications, white PCBs enhance light reflection, potentially improving the overall luminous efficacy of LED products.
2 Medical Devices
The high contrast provided by white PCBs is particularly valuable in medical devices, where precision and ease of inspection are crucial.
3 Aerospace and Defense
White PCBs are gaining traction in aerospace and defense applications due to their heat-reflective properties and high visibility for inspection and maintenance.
4 Consumer Electronics
Many high-end consumer electronics, particularly those with transparent or translucent casings, are utilizing white PCBs for their aesthetic appeal.
5 Automotive Electronics
The automotive industry is adopting white PCBs in various applications, especially in lighting systems and display units.
Operation of Applying White Solder Mask

The application of white solder mask requires precision and attention to detail to ensure optimal results.
1 Surface Preparation
Before applying the solder mask, the PCB surface must be thoroughly cleaned and prepared to ensure proper adhesion.
2 Solder Mask Application
The white solder mask is typically applied using screen printing or photoimaging techniques. The choice depends on the complexity of the board and the required precision.
3 Curing Process
After application, the solder mask undergoes a curing process, usually involving exposure to UV light and heat treatment to achieve the desired hardness and durability.
4 Quality Control
Post-curing, the boards undergo rigorous quality control checks to ensure uniform coverage, proper thickness, and absence of defects.
7. Challenges & Considerations
While white PCBs offer numerous advantages, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
1 UV Sensitivity
White solder masks can be more sensitive to UV light, potentially leading to yellowing over time if not properly formulated or protected.
2 Cost Considerations
White PCBs may come at a slightly higher cost compared to traditional green PCBs due to the specialized materials and potential additional processing steps.
3 Optical Considerations
In some applications, the high reflectivity of white PCBs might interfere with certain optical sensors or components.
4 Manufacturing Complexity
Achieving a uniform, defect-free white surface can be more challenging than with green solder masks, potentially leading to higher rejection rates in manufacturing.
White PCB vs. Traditional Green PCB

To fully appreciate the impact of white PCBs, it’s essential to compare them directly with traditional green PCBs.
1 Visibility and Inspection
White PCBs offer superior contrast, making component markings, traces, and solder joints more visible. This can lead to easier assembly, inspection, and troubleshooting compared to green PCBs.
2 Thermal Properties
The higher reflectivity of white PCBs can contribute to better heat management in some applications, potentially offering a slight advantage over green PCBs in terms of thermal performance.
3 Aesthetic Considerations
White PCBs provide a modern, clean look that can be more visually appealing in certain applications, especially where the PCB is visible in the final product.
4 Manufacturing and Cost
While the manufacturing process is similar, white PCBs may require more precise control and potentially more expensive materials, leading to a slight cost premium over green PCBs.
5 Industry Adoption
Green PCBs still dominate the market due to their long-standing use and familiarity. However, white PCBs are gaining ground, especially in specific sectors like LED lighting and high-end consumer electronics.
Future Trends in White PCB Technology
The future of white PCB technology looks promising, with several trends emerging:
1 Advanced Materials
Research is ongoing to develop white solder mask materials with improved UV resistance, thermal properties, and durability.
2 Integration with Flexible and Rigid-Flex PCBs
As flexible and rigid-flex PCBs become more prevalent, we can expect to see white solder mask options for these advanced board types.
3 Enhanced Printability
Improvements in white solder mask formulations are likely to enhance the ability to print high-resolution text and graphics directly on the board surface.
4 Smart PCB Integration
As IoT and smart devices proliferate, white PCBs may play a role in integrating visual indicators or even display elements directly into the board surface.
5 Sustainability Considerations
Future developments may focus on creating more environmentally friendly white solder mask materials, aligning with the growing emphasis on sustainability in electronics manufacturing.
Conclusion
White PCBs represent a significant evolution in printed circuit board technology. Their enhanced visibility, aesthetic appeal, and potential performance benefits are driving adoption across various industries. While challenges exist, ongoing research and development are likely to address these issues, further solidifying the place of white PCBs in modern electronics.
As we look to the future, white PCBs are poised to play an increasingly important role in electronic design and manufacturing. Their ability to combine functionality with aesthetics makes them a compelling choice for innovators pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in electronics. Whether it’s in the next generation of LED lighting, cutting-edge medical devices, or sleek consumer electronics, white PCBs are illuminating the path forward in the world of electronic innovation.
