Resistors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, playing a crucial role in controlling electrical current flow. Accurate identification of these components is essential for electronics enthusiasts, engineers, and technicians working with electrical systems.

Resistor Fundamentals
Basic Characteristics of Resistors
Key Physical Properties
| Property | Description | Significance |
| Resistance | Opposition to current flow | Determines circuit behavior |
| Power Rating | Maximum power dissipation | Prevents component failure |
| Tolerance | Accuracy of resistance value | Impacts circuit precision |
| Temperature Coefficient | Resistance variation with temperature | Critical for stable performance |
Color Code Identification Method
Standard Resistor Color Coding System
Color Band Interpretation
| Band Position | Meaning | Value Representation |
| 1st Band | First Significant Digit | 0-9 |
| 2nd Band | Second Significant Digit | 0-9 |
| 3rd Band | Multiplier | Decimal place shift |
| 4th Band | Tolerance | Percentage accuracy |
| 5th Band | Temperature Coefficient | Performance variation |
Detailed Color Code Decoding
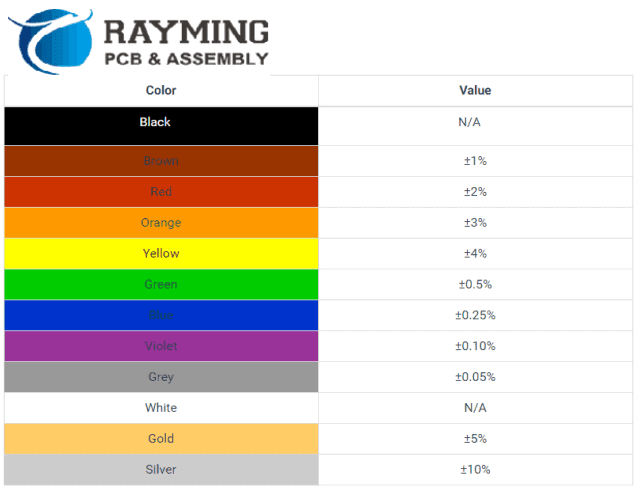
Color to Value Mapping
| Color | Numeric Value | Multiplier | Tolerance |
| Black | 0 | × 1 | ±1% |
| Brown | 1 | × 10 | ±1% |
| Red | 2 | × 100 | ±2% |
| Orange | 3 | × 1,000 | ±3% |
| Yellow | 4 | × 10,000 | ±4% |
| Green | 5 | × 100,000 | ±0.5% |
| Blue | 6 | × 1,000,000 | ±0.25% |
| Violet | 7 | × 10,000,000 | ±0.1% |
| Gray | 8 | × 100,000,000 | ±0.05% |
| White | 9 | × 1,000,000,000 | ±5% |
Advanced Identification Techniques
Measurement Tools and Methods
Identification Equipment
| Tool | Purpose | Accuracy | Recommended Use |
| Multimeter | Resistance Measurement | 卤0.1惟 | Direct Resistance Check |
| LCR Meter | Precise Component Analysis | 卤0.1% | Comprehensive Testing |
| Digital Caliper | Physical Dimension Verification | 卤0.01mm | Size and Type Confirmation |
| Microscope | Surface Detail Examination | Optical Precision | Fine Detail Analysis |
Resistor Type Classification
Comprehensive Resistor Taxonomy
Main Resistor Categories
- Fixed Resistors
- Carbon Composition
- Metal Film
- Wire Wound
- Precision Metal Strip
- Variable Resistors
- Potentiometers
- Trimpots
- Rheostats
- Special Purpose Resistors
- Current Sensing
- High Voltage
- Power Resistors
- Precision Reference
Physical Characteristics Analysis
Dimensional and Structural Identification
Key Physical Indicators
| Characteristic | Identification Criteria | Significance |
| Body Material | Ceramic, Plastic, Metal | Indicates Construction Type |
| Terminal Style | Axial, Surface Mount | Mounting Configuration |
| Body Shape | Cylindrical, Rectangular | Determines Installation Method |
| Surface Marking | Printed Resistance Values | Direct Identification |
Temperature and Environmental Considerations
Factors Affecting Resistor Identification
Environmental Impact Assessment
- Temperature Sensitivity
- Humidity Resistance
- Mechanical Stress Tolerance
- Aging Effects
Precision Identification Protocols

Step-by-Step Identification Process
Comprehensive Verification Method
- Visual Inspection
- Color Code Decoding
- Dimensional Measurement
- Electrical Measurement
- Comparative Analysis
Common Identification Challenges
Troubleshooting Identification Difficulties
Resolution Strategies
| Challenge | Diagnostic Approach | Recommended Solution |
| Faded Markings | Microscopic Examination | Alternative Measurement Methods |
| Surface Damage | Comparative Analysis | Specialized Testing Equipment |
| Unusual Configurations | Historical Reference | Manufacturer Documentation |
Advanced Digital Identification Technologies
Emerging Identification Methods
Technological Approaches
- Machine Learning Recognition
- Spectral Analysis
- Computer Vision Techniques
- Automated Scanning Systems
Professional Best Practices
Recommended Identification Techniques
- Use Multiple Verification Methods
- Maintain Comprehensive Documentation
- Invest in Precision Measurement Tools
- Stay Updated on New Technologies
Safety Considerations
Handling and Identification Precautions
Critical Safety Guidelines
- Use Proper Personal Protective Equipment
- Avoid Direct Contact with Energized Components
- Discharge Capacitors Before Measurement
- Work in Well-Ventilated Areas
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How Accurate Are Color Codes for Resistor Identification?
A1: Color codes are generally 95-99% accurate when properly interpreted. However, factors like age, wear, and manufacturing variations can affect precision.
Q2: Can I Identify a Resistor Without a Multimeter?
A2: While a multimeter provides the most accurate measurement, color codes and physical characteristics can offer reliable preliminary identification.
Q3: What’s the Most Common Mistake in Resistor Identification?
A3: Misreading color bands due to improper orientation or misunderstanding the color-to-value mapping is the most frequent identification error.
Q4: How Do Surface Mount Resistors Differ in Identification?
A4: Surface mount resistors typically use numerical codes instead of color bands, requiring different identification techniques and specialized knowledge.
Q5: Are There Universal Identification Standards?
A5: While color coding is widely used, international standards like IEC and ANSI provide comprehensive guidelines for resistor marking and identification.
Conclusion
Resistor identification is a nuanced skill combining visual analysis, technical knowledge, and precision measurement techniques. By understanding the comprehensive approach outlined in this guide, professionals and enthusiasts can confidently and accurately identify resistors across various applications and environments.

