Electronic Contract Manufacturing: Benefits, Process & Cost Guide
At RayMing, we streamline contract manufacturing through efficient processes, optimized supply chains, and consistent delivery of high-quality finished products.
After spending 20 years in the PCB industry, I’ve watched electronic contract manufacturing transform from a simple outsourcing option into a strategic business necessity. The global electronic contract manufacturing market hit $528.93 billion in 2024 and is racing toward $818.42 billion by 2029. That’s not just growth—it’s a fundamental shift in how electronics get made.
Whether you’re a startup founder staring at your first prototype or a procurement manager at an established OEM looking to optimize production costs, understanding electronic contract manufacturing can save you months of headaches and significant capital. This guide breaks down everything you need to know—from picking the right partner to understanding what drives your final quote.
What is Electronic Contract Manufacturing?
Electronic contract manufacturing (ECM) happens when specialized companies handle the design, manufacturing, testing, and distribution of electronic components and assemblies for other businesses. These contract manufacturers—often called CEMs (Contract Electronics Manufacturers) or EMS providers—become your production arm while you focus on what you do best: developing products and building your brand.
Think of it this way: Apple designs the iPhone, but Foxconn manufactures it. That’s electronic contract manufacturing at scale.
The concept emerged in 1961 when SCI Systems in Huntsville, Alabama pioneered the model. Since then, ECM has evolved from basic board assembly into comprehensive partnerships covering everything from initial design assistance to warranty repairs.
ECM vs. EMS vs. OEM: Clearing Up the Confusion
These terms get thrown around interchangeably, but they mean different things:
| Term | Definition | What They Do |
|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | The brand owner | Designs products, owns IP, handles marketing and sales |
| ECM (Electronic Contract Manufacturer) | Production partner | Manufactures electronics based on OEM specifications |
| EMS (Electronic Manufacturing Services) | Service provider | Offers full-spectrum manufacturing services including design |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Design + manufacturing partner | Creates complete product designs that clients can brand as their own |
The practical difference? EMS typically offers more comprehensive services than a basic ECM, while ODMs bring their own designs to the table. When Apple works with Foxconn, that’s an ECM relationship. When a startup licenses a smartwatch design from Compal and puts their logo on it, that’s ODM.
EMS Products We Served
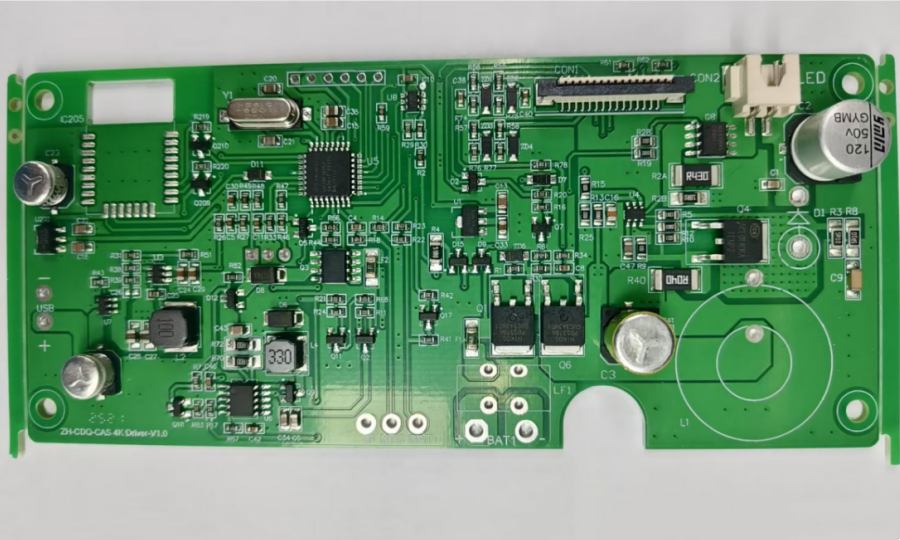




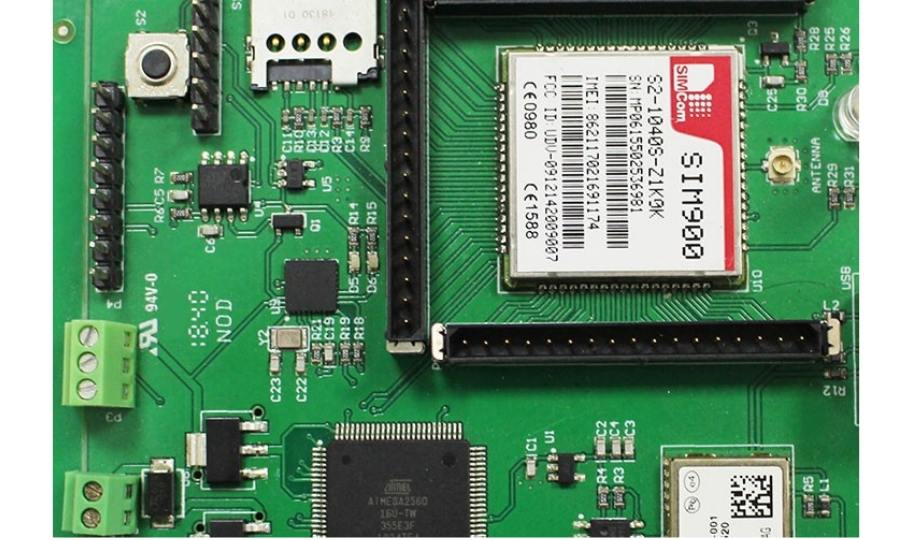
In-Vitro Diagnostic Equipment PCBA

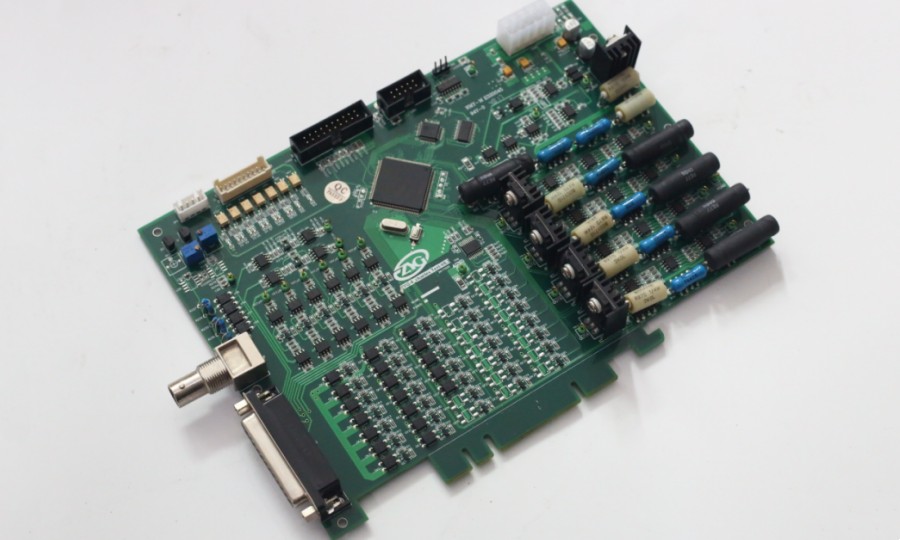
Signal Processing PCBA manufacturing
Core Services Offered by Electronic Contract Manufacturers
A capable electronic contract manufacturer should cover most or all of these service areas:
Design and Engineering Support
- PCB Layout and Design: Converting schematics into manufacturable board designs
- DFM (Design for Manufacturing) Review: Identifying potential production issues before they become expensive problems
- Prototyping: Building test units to validate your design
- Component Engineering: Selecting parts that balance performance, availability, and cost
Manufacturing Operations
| Service | Description | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| SMT Assembly | Surface mount technology for modern compact components | Smartphones, IoT devices, medical equipment |
| Through-Hole Assembly | Traditional component insertion for connectors and high-power parts | Industrial controls, power supplies |
| Mixed Technology | Combination of SMT and THT on the same board | Complex industrial systems, automotive electronics |
| Box Build Assembly | Complete system integration including enclosures | Consumer products, industrial equipment |
| Cable and Wire Harness | Custom interconnect assemblies | Automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery |
Testing and Quality Assurance
Quality testing separates professional ECM providers from budget assemblers. Look for:
- AOI (Automated Optical Inspection): Machine vision checking for solder defects
- X-Ray Inspection: Essential for BGA packages and hidden solder joints
- ICT (In-Circuit Testing): Verifying component values and connections
- Functional Testing: Making sure the board actually works as intended
- Environmental Testing: Temperature cycling, humidity, vibration
- Burn-in Testing: Running boards under stress to catch early failures
Supply Chain Management
Modern electronic contract manufacturing extends well beyond assembly lines:
- Component sourcing and procurement
- Inventory management and buffer stock
- Obsolescence monitoring and lifecycle management
- Logistics and global distribution
- After-sales support and repair services
EMS Calculator & Service Finder
RayPCB Engineering Tools
Answer a few questions to find the right EMS services for your project.
Recommended: Quick-Turn Prototype
Suggested Services:
Get an instant estimate for your PCB assembly project.
💵 Assembly Cost Estimate
*Estimate only. Final quote may vary based on detailed specifications and BOM review.
Calculate estimated production lead time for your EMS project.
⏱️ Estimated Lead Time
Compare pricing across different production volumes to optimize your order quantity.
📊 Volume Pricing Comparison
| Quantity | Unit Price | Total | Savings |
|---|
Ready to start your project? Get a detailed quote from our engineering team.
The Electronic Contract Manufacturing Process
Understanding how ECM works helps you prepare better documentation and set realistic timelines. Here’s what actually happens once you engage a contract manufacturer:
Phase 1: Quoting and Design Review (1-2 Weeks)
You submit your Gerber files, BOM (Bill of Materials), and assembly drawings. The ECM’s engineering team reviews everything for manufacturability. Expect questions about:
- Component availability and lead times
- Acceptable alternatives for hard-to-source parts
- Panelization preferences
- Testing requirements
- Volume projections
Pro tip: A thorough DFM check at this stage catches 80% of potential production issues. Don’t skip it to save time—you’ll pay for it later.
Phase 2: Procurement and Planning (2-6 Weeks)
Once you approve the quote, procurement begins. Lead times depend heavily on component availability. Standard parts might be in stock; specialized ICs could take 12-20 weeks.
During this phase, the manufacturer also:
- Creates production documentation
- Designs test fixtures
- Programs pick-and-place machines
- Sets up solder paste stencils
Phase 3: Production and Assembly
The assembly process follows a predictable sequence:
For SMT Assembly:
- Solder paste application via stencil printing
- Component placement using pick-and-place machines
- Reflow soldering through temperature-controlled ovens
- Automated optical inspection
- X-ray inspection (for BGA and hidden joints)
For Through-Hole Components:
- Manual or automated component insertion
- Wave soldering or selective soldering
- Touch-up and inspection
For Mixed Technology: The process typically runs SMT first, then through-hole, with inspection at each stage.
Phase 4: Testing and Quality Control
Every board should go through at minimum:
- Visual inspection
- Automated optical inspection
- Functional testing per your test specification
Medical, aerospace, and automotive applications require additional testing protocols mandated by industry standards.
Phase 5: Packaging and Delivery
Finished products get packaged according to your specifications—whether that’s bulk trays for your own integration line or retail-ready packaging for direct shipment to customers.
Benefits of Electronic Contract Manufacturing
Here’s why the electronic contract manufacturing market continues growing at nearly 10% annually:
Cost Reduction
The numbers don’t lie. Outsourcing to electronic contract manufacturers typically reduces manufacturing costs by 30-50% compared to in-house production. This comes from:
| Cost Factor | In-House | ECM Outsourced |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Equipment | $2-10M investment | $0 (included in service) |
| Facility Costs | Monthly overhead | Pay per unit |
| Labor Training | Ongoing expense | Manufacturer’s responsibility |
| Component Pricing | Low-volume rates | Volume discounts passed through |
| Inventory Carrying | Your balance sheet | Often held by ECM |
Scalability and Flexibility
This is where electronic contract manufacturing really shines. You can:
- Start with 50-unit prototypes
- Scale to 5,000 units for market launch
- Ramp to 50,000 units when demand spikes
- Scale back during slow periods
All without changing your fixed costs or workforce.
Access to Advanced Technology
Modern SMT lines cost millions. X-ray inspection equipment, clean rooms, and specialized test systems add millions more. Through ECM partnerships, you get access to:
- Latest-generation pick-and-place equipment
- Advanced inspection technologies
- Certified processes (ISO, IPC, AS9100)
- Specialized capabilities (HDI, flex circuits, RF assembly)
Faster Time-to-Market
Experienced electronic contract manufacturers have established processes and qualified supply chains. A new product that might take 6-9 months to set up internally can often launch in 3-4 months through an ECM partner.
Risk Mitigation
Diversifying production reduces your exposure to:
- Supply chain disruptions
- Single-point-of-failure facilities
- Regulatory compliance gaps
- Quality control inconsistencies
Electronic Contract Manufacturing Cost Factors

Understanding what drives your quote helps you optimize both design and procurement decisions.
Primary Cost Components
| Component | Typical % of Total | What Affects It |
|---|---|---|
| Materials/Components | 60-75% | Component selection, volume, market conditions |
| Direct Labor | 10-20% | Assembly complexity, geographic location |
| Manufacturing Overhead | 5-10% | Equipment utilization, facility costs |
| Testing | 3-8% | Test coverage requirements |
| Profit Margin | 5-15% | Volume commitments, relationship length |
Pricing Models in Electronic Contract Manufacturing
Most electronic contract manufacturers use “cost-plus” pricing—they calculate their costs and add a margin. Here’s how that typically works:
Cost-Plus Example:
- Material cost: $450
- Labor and overhead: $90
- Total cost: $540
- At 25% margin: $540 ÷ 0.75 = $720 per unit
Volume Impact: As volumes increase, your cost per unit decreases substantially:
| Volume | Approximate Unit Cost Reduction |
|---|---|
| Prototype (10-50 units) | Baseline |
| Low Volume (100-500 units) | 15-25% lower |
| Medium Volume (1,000-5,000 units) | 30-40% lower |
| High Volume (10,000+ units) | 45-55% lower |
Hidden Cost Considerations
Watch for these often-overlooked factors:
- NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering): Setup costs, fixture development, programming
- Tooling: Stencils, test fixtures, custom jigs
- Minimum Order Quantities: Component MOQs can inflate small-run costs
- Shipping and Tariffs: Especially relevant for offshore manufacturing
- Quality Costs: Rework, rejects, warranty returns
Domestic vs. Offshore Manufacturing
The “China is cheaper” assumption needs reality-checking:
| Factor | Offshore (Asia) | Domestic (US/Europe) |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Labor | 50-70% lower | Higher base cost |
| Shipping | $2-5K+ per shipment | Minimal |
| Lead Time | 8-12 weeks typical | 2-4 weeks typical |
| Communication | Time zone challenges | Same-day response |
| IP Protection | Variable enforcement | Strong legal framework |
| Quality Control | Requires oversight | Generally consistent |
| Tariffs | 7.5-25% on electronics | None |
| Minimum Orders | Often higher | More flexible |
For many products, especially those with moderate volumes or tight timelines, domestic electronic contract manufacturing delivers better total value despite higher per-unit labor costs.
How to Choose an Electronic Contract Manufacturer

Selecting the right ECM partner matters more than squeezing the last few percent from your quote. Here’s what to evaluate:
Technical Capabilities Checklist
✅ Required certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 13485 for medical, AS9100 for aerospace)
✅ Equipment matching your technology requirements
✅ Testing capabilities aligned with your quality needs
✅ Experience with similar product types
✅ Design support services
Business Considerations
✅ Financial stability and track record
✅ Transparent pricing models
✅ Intellectual property protection policies
✅ Communication responsiveness
✅ Scalability for your growth plans
Red Flags to Watch
❌ Reluctance to provide customer references
❌ Unusually low quotes (often means quality shortcuts)
❌ No DFM feedback on your design
❌ Poor documentation practices
❌ Excessive NDAs before sharing basic information
Questions to Ask Potential ECM Partners
- What percentage of your production is in my industry sector?
- How do you handle component obsolescence?
- What’s your typical on-time delivery rate?
- Can I tour your facility?
- How do you manage quality escapes?
- What ERP/MES systems do you use?
- How are engineering changes handled mid-production?
Industries Served by Electronic Contract Manufacturing
Electronic contract manufacturing supports virtually every sector requiring electronics:
| Industry | Typical Requirements | Key Certifications |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | Cleanroom, traceability, biocompatibility | ISO 13485, FDA registration |
| Automotive | High reliability, long lifecycles, environmental stress | IATF 16949, AEC-Q standards |
| Aerospace/Defense | Mil-spec compliance, security clearances | AS9100, ITAR registration |
| Industrial | Ruggedization, long product life | ISO 9001, IPC Class 3 |
| Consumer Electronics | High volume, cost optimization | ISO 9001, UL/CSA |
| Telecommunications | RF expertise, EMC compliance | ISO 9001, carrier approvals |
| IoT/Wearables | Miniaturization, power optimization | Varies by application |
Common Mistakes When Working with Electronic Contract Manufacturers
Learning from others’ failures saves time and money. Here are the mistakes I see most frequently:
Underestimating Lead Times
Components don’t magically appear. Lead times for semiconductors can stretch to 52+ weeks during shortages. Plan procurement early, identify long-lead items upfront, and consider buffer inventory for critical parts.
Incomplete Documentation
Missing information delays quotes and causes production errors. Your BOM should include:
- Approved manufacturer part numbers
- Acceptable alternates clearly marked
- Reference designators matching your Gerber files
- Quantities (including attrition allowance)
- Special handling notes for moisture-sensitive components
Chasing the Lowest Quote
The cheapest bid often becomes the most expensive choice. Hidden costs emerge through:
- Quality issues requiring rework
- Missed delivery dates disrupting your launch
- Component substitutions affecting performance
- Poor communication wasting your engineering time
Evaluate total cost of ownership, not just unit price.
Ignoring Design for Manufacturing
Your brilliant design might be impossible—or needlessly expensive—to manufacture. Common DFM issues include:
- Component spacing too tight for rework
- Via-in-pad requiring filling (adds cost)
- Panelization that wastes material
- Testpoint accessibility problems
- Thermal management overlooked
Engage your ECM partner early for DFM review. Changes are cheap in design, expensive in production.
Poor Communication Practices
Electronic contract manufacturers aren’t mind readers. Document your requirements explicitly:
- Acceptable quality levels (defects per million)
- Cosmetic standards and customer-facing surfaces
- Serialization and traceability requirements
- Packaging and labeling specifications
- Shipping and handling instructions
Write it down. Assumptions kill projects.
Building an Effective RFQ Package
Your Request for Quote package determines quote accuracy and manufacturing success. Here’s what to include:
Essential Documents
| Document | Format | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Gerber Files | RS-274X or ODB++ | PCB fabrication data |
| Bill of Materials | Excel with standard columns | Component purchasing |
| Assembly Drawing | Component placement and polarity | |
| Schematic | PDF (optional) | Engineering reference |
| Test Specification | PDF or Word | Quality requirements |
| Mechanical Drawing | PDF or STEP | Enclosure integration |
BOM Best Practices
A well-structured BOM prevents procurement delays:
| Item | Qty | Ref Des | Manufacturer | MPN | Description | Alternates |
|------|-----|---------|--------------|-----|-------------|------------|
| 1 | 4 | C1-C4 | Murata | GRM155R71C104KA88D | 0.1uF 16V 0402 | TDK C1005X5R1C104K |
| 2 | 2 | R1,R2 | Yageo | RC0402FR-0710KL | 10K 1% 0402 | Generic OK |Include alternates for critical components. Generic resistance and capacitance values can often be multi-sourced, but specify when precision matters.
Volume and Forecast Information
Help your ECM partner plan capacity and procurement:
- Prototype quantity needed
- First production run timing and volume
- 12-month volume forecast
- Peak demand expectations
- Product lifetime estimate
Better forecasting leads to better pricing and inventory planning.
Future Trends in Electronic Contract Manufacturing
The ECM industry continues evolving. Here’s what’s shaping the next five years:
Industry 4.0 Integration
Smart factories with IoT-connected equipment enable real-time production monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated quality tracking. Leading electronic contract manufacturers are investing heavily in digital transformation.
Reshoring and Nearshoring
Supply chain disruptions during 2020-2022 accelerated the trend toward regional manufacturing. The U.S. CHIPS Act and similar initiatives are driving renewed investment in domestic electronic manufacturing capacity.
Sustainability Focus
Environmental regulations and customer expectations are pushing ECM providers toward:
- Lead-free and halogen-free processes
- Energy-efficient manufacturing
- Circular economy practices
- Carbon footprint reduction
Advanced Technologies
Electronic contract manufacturers increasingly need capabilities for:
- High-density interconnect (HDI) boards
- Embedded components
- 5G and mmWave assemblies
- Advanced packaging (SiP, 2.5D, 3D)
Useful Resources for Finding ECM Partners
Here are databases and directories where you can research and compare electronic contract manufacturing providers:
| Resource | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| ThomasNet | Comprehensive U.S. supplier directory with filtering by certification and capability | thomasnet.com |
| GlobalSpec | Technical specifications-based search with 1,400+ EMS providers | globalspec.com |
| VentureOutsource | Specialized contract electronics directory with detailed capability profiles | ventureoutsource.com |
| EMS-Europe.info | Free directory focused on European EMS providers | ems-europe.info |
| HardwareBee | EMS company directory with design service filtering | hardwarebee.com |
| Ensun | AI-powered supplier matching platform | ensun.io |
Industry Standards and Certifications Reference
| Standard | Purpose | Applies To |
|---|---|---|
| IPC-A-610 | Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies | All PCBA |
| IPC-J-STD-001 | Soldering Requirements | All soldered assemblies |
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management Systems | General manufacturing |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Device Quality | Medical electronics |
| AS9100 | Aerospace Quality | Aerospace/defense |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive Quality | Automotive electronics |
Frequently Asked Questions About Electronic Contract Manufacturing
What’s the minimum order quantity for electronic contract manufacturing?
Most electronic contract manufacturers accommodate prototypes starting at 5-25 units, though pricing per unit will be significantly higher than production volumes. For cost-effective production runs, expect minimums of 100-500 units depending on complexity. Some manufacturers specialize in low-volume, high-mix production while others focus on high-volume runs.
How long does the typical electronic contract manufacturing process take?
Timeline varies by complexity and component availability. Prototype builds typically take 2-4 weeks after materials arrive. First production runs add 1-2 weeks for process validation. Material lead times currently range from in-stock to 20+ weeks for constrained components. A realistic estimate from quote acceptance to first delivery is 8-12 weeks for most projects.
Should I choose a domestic or offshore electronic contract manufacturer?
It depends on your priorities. Offshore manufacturers in Asia offer lower per-unit costs for high volumes but come with longer lead times, shipping costs, communication challenges, and potential IP risks. Domestic manufacturers provide faster response times, easier communication, and better IP protection. For many products with volumes under 10,000 units annually, domestic manufacturers often deliver better total value.
What files do I need to provide to get an electronic contract manufacturing quote?
At minimum, you need: Gerber files (or ODB++ or IPC-2581), Bill of Materials with manufacturer part numbers, assembly drawings showing component placement and orientation, and a specification document covering testing requirements and acceptable quality levels. Additional documentation like schematics, 3D models, and test procedures helps ensure accurate quoting.
How do I protect my intellectual property when using electronic contract manufacturing?
Start with a comprehensive NDA before sharing detailed designs. Work with manufacturers in jurisdictions with strong IP enforcement. Consider splitting production across multiple suppliers so no single partner has complete product knowledge. Avoid sharing more information than necessary—Gerber files for fabrication don’t require full schematics. Document everything and maintain your own design archives.
Making Your ECM Partnership Work
After working with dozens of electronic contract manufacturers over my career, here’s what separates successful partnerships from troubled ones:
Communicate early and often. The best manufacturers want to help you succeed. Share your roadmap, discuss concerns openly, and treat them as partners rather than vendors.
Invest in documentation. Clear specs, complete BOMs, and thorough test procedures prevent misunderstandings. The time you spend on documentation saves multiples in production issues.
Visit the facility. Nothing replaces walking the production floor. You’ll learn more in one factory tour than a hundred email exchanges.
Start small, then scale. Run a pilot before committing to large volumes. Iron out process issues while stakes are low.
Build relationships. When supply chains get tight or you need expedited support, relationships matter. The manufacturers who go above and beyond for you are the ones who know you’ll be there for them too.
Electronic contract manufacturing isn’t just about outsourcing production—it’s about building a supply chain that can scale with your business, adapt to market changes, and deliver quality products consistently. Choose your partners wisely, invest in the relationship, and you’ll have a competitive advantage that’s hard to replicate.
Key Certifications to Look For
When evaluating electronic contract manufacturing partners, certifications provide third-party validation of capabilities:
Quality Management Certifications
| Certification | What It Covers | Who Needs It |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | General quality management system | All industries |
| ISO 13485:2016 | Medical device quality management | Medical device manufacturers |
| AS9100D | Aerospace quality management | Aerospace and defense |
| IATF 16949:2016 | Automotive quality management | Automotive suppliers |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental management | Companies with sustainability goals |
Manufacturing Standards
| Standard | Purpose | Application |
|---|---|---|
| IPC-A-610 | Acceptability criteria for electronic assemblies | All PCB assembly |
| IPC/WHMA-A-620 | Wire and cable assembly requirements | Cable and harness manufacturers |
| J-STD-001 | Soldering requirements | All soldering operations |
| IPC-7711/7721 | Rework and repair guidelines | Rework operations |
Special Requirements
Some applications require additional certifications:
- ITAR Registration: Required for defense-related manufacturing
- FDA Registration: Required for medical device manufacturers
- UL Certification: For products requiring safety certification
- RoHS/REACH Compliance: Environmental regulations for EU market
The Bottom Line on Electronic Contract Manufacturing
The electronic contract manufacturing industry exists because specialization creates value. Companies that try to do everything—design, manufacture, market, sell, support—spread themselves thin. By partnering with experienced electronic contract manufacturers, you leverage their expertise, equipment, and economies of scale while focusing your resources on innovation and customer relationships.
The key questions to ask yourself before selecting an ECM partner:
- What’s my real priority? Cost, speed, quality, or flexibility?
- What’s my realistic volume projection? Be honest—inflated forecasts lead to wrong partner selection.
- How critical is communication? Time zone differences matter when problems arise.
- What’s my risk tolerance? Single-source vs. dual-source strategies have different cost-risk tradeoffs.
- How long is this product’s lifecycle? Long-lifecycle products need partners committed to continuity.
There’s no perfect electronic contract manufacturer—only the right fit for your specific situation. Take time to evaluate options, visit facilities when possible, start with smaller projects to build trust, and treat your ECM partner as an extension of your team.
The companies that thrive in today’s competitive electronics market are the ones that build strong electronic contract manufacturing relationships. Your ECM partner’s success is your success, and vice versa.