What are Flexible PCBs?
Flexible printed circuit boards, also known as flex PCBs or flexible electronics, are thin, bendable circuit boards that can be shaped to fit into tight spaces or conform to unique product designs. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, flexible PCBs are made with a flexible base material, typically a plastic film like polyimide, which allows them to bend, fold, and twist without breaking.
Components of Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs consist of several key components:
- Base material (substrate)
- Conductive layers
- Coverlay or protective coating
- Adhesives
- Circuitry and components

Learn more about:
Let’s take a closer look at each of these components:
| Component | Description | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Base material | The flexible substrate that forms the foundation of the PCB | Polyimide, Polyester, LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer) |
| Conductive layers | Thin layers of conductive material that form the circuit paths | Copper, Silver, Aluminum |
| Coverlay | A protective layer that insulates and protects the circuitry | Polyimide, Epoxy |
| Adhesives | Materials used to bond layers together | Acrylic, Epoxy |
| Circuitry and components | The actual electronic components and traces that make up the circuit | Various metals and electronic components |
Types of Flexible PCBs

Flexible PCBs come in various types, each designed to meet specific application requirements:
Single-sided Flex PCBs
Single-sided flex PCBs have a single conductive layer on one side of the flexible substrate. They are the simplest and most cost-effective type of flexible PCB.
Double-sided Flex PCBs
Double-sided flex PCBs have conductive layers on both sides of the substrate, allowing for more complex circuit designs and higher component density.
Multilayer Flex PCBs
Multilayer flex PCBs consist of three or more conductive layers, separated by insulating layers. They offer the highest level of circuit density and complexity.
Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs combine both rigid and flexible board technologies in a single circuit board. They feature areas of flexible circuitry connected to rigid board sections.
Here’s a comparison of these types:
| Type | Complexity | Cost | Flexibility | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-sided | Low | Low | High | Simple consumer electronics, wearables |
| Double-sided | Medium | Medium | Medium | Smartphones, tablets |
| Multilayer | High | High | Low-Medium | Advanced medical devices, aerospace equipment |
| Rigid-Flex | Very High | Very High | Variable | Military equipment, complex industrial machinery |
Manufacturing Process of Flexible PCBs

The manufacturing process for flexible PCBs differs from that of rigid PCBs due to the unique materials and requirements involved. Here’s an overview of the main steps:
- Material preparation
- Imaging and etching
- Coverlay application
- Drilling and plating
- Surface finishing
- Assembly and testing
Each of these steps requires specialized equipment and techniques to ensure the flexibility and durability of the final product.
Advantages of Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs offer numerous advantages over their rigid counterparts:
1. Space and Weight Savings
Flexible PCBs can be bent, folded, or shaped to fit into tight or irregularly shaped spaces, allowing for more compact and lightweight product designs.
2. Increased Reliability
The ability to flex reduces stress on components and solder joints, potentially increasing the overall reliability and lifespan of the device.
3. Improved Thermal Management
Flexible PCBs can dissipate heat more effectively than rigid boards, which can lead to better thermal management in electronic devices.
4. Enhanced Design Freedom
Designers have more freedom to create unique and innovative product shapes and form factors when using flexible PCBs.
5. Resistance to Vibration and Movement
The flexible nature of these PCBs makes them more resistant to vibration and movement, which is crucial in applications like automotive electronics or wearable devices.
| Advantage | Description | Impact on Design |
|---|---|---|
| Space and Weight Savings | Allows for compact and lightweight designs | Enables smaller, more portable devices |
| Increased Reliability | Reduces stress on components and solder joints | Longer product lifespan, fewer failures |
| Improved Thermal Management | Better heat dissipation | Enhanced performance in high-power applications |
| Enhanced Design Freedom | Allows for unique and innovative product shapes | Enables creative and ergonomic designs |
| Resistance to Vibration | Better performance in high-vibration environments | Ideal for automotive and aerospace applications |
Applications of Flexible PCBs
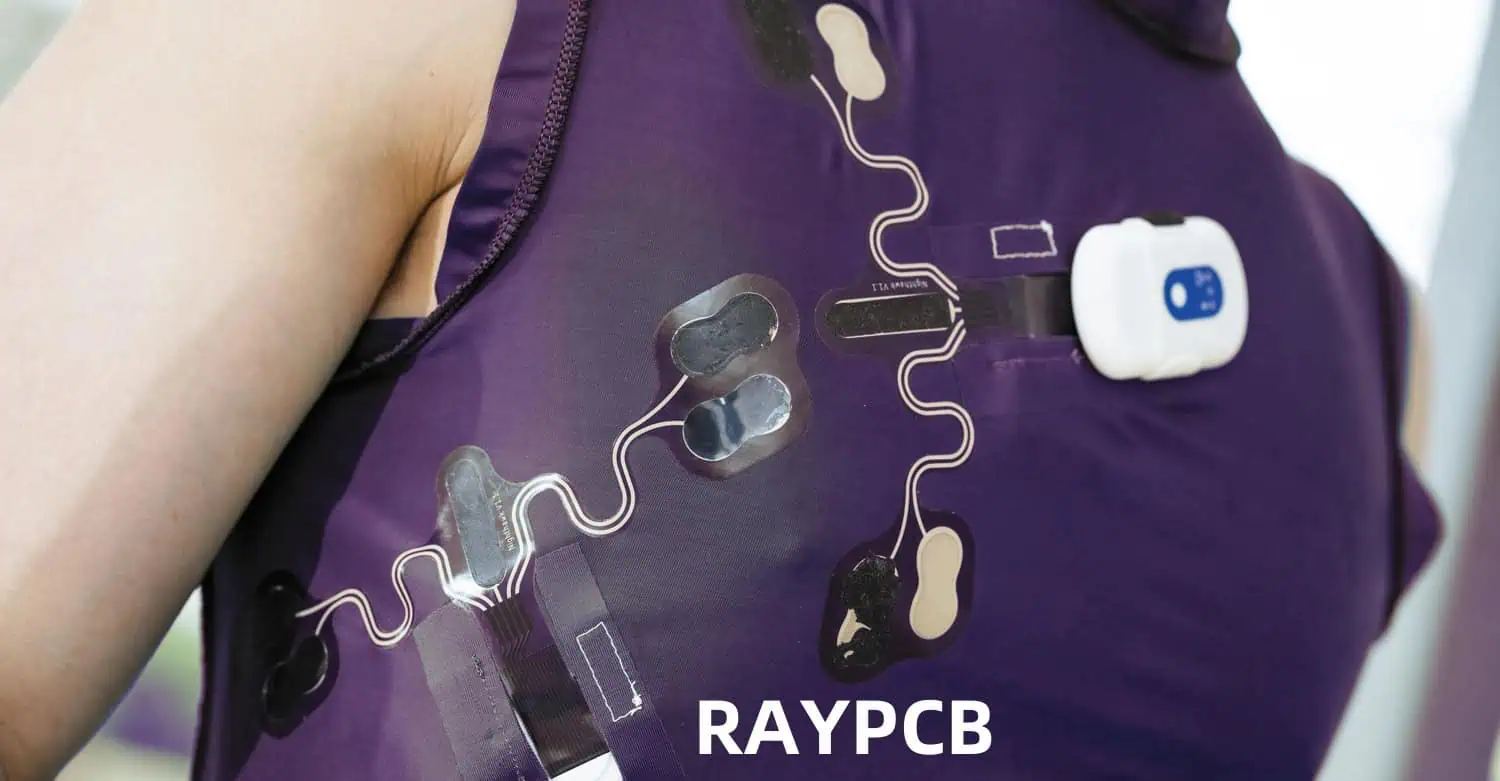

Flexible PCBs have found their way into a wide range of industries and applications:
Consumer Electronics
- Smartphones and tablets
- Wearable devices (smartwatches, fitness trackers)
- Digital cameras
- Flexible displays
Automotive Industry
- Dashboard electronics
- Engine control systems
- Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)
Medical Devices
- Implantable devices
- Hearing aids
- Portable diagnostic equipment
Aerospace and Defense
- Satellite systems
- Aircraft avionics
- Military communication devices
Industrial Equipment
- Robotics
- Flexible solar panels
- Industrial control systems
Here’s a table summarizing the applications across different industries:
| Industry | Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphones, wearables, cameras | Compact design, lightweight |
| Automotive | Dashboard electronics, engine control | Vibration resistance, space-saving |
| Medical Devices | Implantables, hearing aids | Biocompatibility, miniaturization |
| Aerospace and Defense | Satellite systems, avionics | Reliability, weight reduction |
| Industrial Equipment | Robotics, solar panels | Durability, design flexibility |
Challenges and Limitations of Flexible PCBs

While flexible PCBs offer many advantages, they also come with their own set of challenges and limitations:
1. Higher Manufacturing Costs
The specialized materials and manufacturing processes required for flexible PCBs often result in higher production costs compared to rigid PCBs.
2. Design Complexity
Designing flexible PCBs requires a different approach and specialized software tools, which can increase the complexity of the design process.
3. Limited Component Options
Not all electronic components are suitable for use with flexible PCBs, which can limit design options in some cases.
4. Durability Concerns
While flexible PCBs are designed to bend, excessive or repeated flexing can potentially lead to fatigue and failure over time.
5. Thermal Management Challenges
Despite improved heat dissipation in some cases, managing heat in densely packed flexible circuits can be challenging.
| Challenge | Description | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Higher Costs | Increased production expenses | Optimize design for mass production, explore new materials |
| Design Complexity | Requires specialized approach and tools | Invest in training, use advanced design software |
| Limited Components | Not all components work with flex PCBs | Develop flex-compatible components, creative design solutions |
| Durability Concerns | Potential fatigue from repeated flexing | Careful design of flex zones, use of strain relief |
| Thermal Management | Heat dissipation in dense circuits | Improved thermal design, use of heat-spreading materials |
Future of Flexible PCBs
The future of flexible PCBs looks promising, with ongoing research and development pushing the boundaries of what’s possible:
Stretchable Electronics
Researchers are working on developing stretchable PCBs that can not only bend but also stretch, opening up new possibilities for wearable and medical devices.
Integration with 3D Printing
Advancements in 3D printing technology may allow for the direct printing of flexible circuits, potentially revolutionizing the manufacturing process.
Improved Materials
New materials are being developed to enhance the performance, durability, and flexibility of PCBs while potentially reducing costs.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Devices
The growth of IoT and smart devices will likely drive further innovation in flexible PCB technology to meet the demand for smaller, more versatile electronics.
Sustainable and Biodegradable PCBs
As environmental concerns grow, there’s increasing research into developing sustainable and even biodegradable flexible PCBs.
Conclusion
Flexible PCBs have indeed revolutionized the electronics industry, enabling the creation of smaller, lighter, and more versatile devices. While they come with their own set of challenges, the advantages they offer in terms of design freedom, reliability, and performance make them an invaluable technology in modern electronics. As research continues and new applications emerge, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of flexible PCBs in the future, further blurring the lines between rigid and flexible electronics.
FAQ
1. Are flexible PCBs more expensive than rigid PCBs?
Yes, flexible PCBs are generally more expensive than rigid PCBs due to the specialized materials and manufacturing processes involved. However, they can offer cost savings in other areas, such as assembly and packaging, due to their space-saving and design flexibility benefits.
2. How durable are flexible PCBs?
Flexible PCBs are designed to be quite durable and can withstand repeated bending and flexing. However, their durability depends on factors such as the materials used, the design of the flex zones, and the specific application. When properly designed and used within their specified parameters, flexible PCBs can be very reliable.
3. Can all electronic components be used with flexible PCBs?
Not all electronic components are suitable for use with flexible PCBs. Some components may be too rigid or heavy, which could cause stress on the flexible substrate. However, many components have been adapted for use with flexible PCBs, and new flex-compatible components are continually being developed.
4. What industries benefit most from flexible PCB technology?
While flexible PCBs have applications across many industries, they are particularly beneficial in consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, aerospace, and wearable technology. These industries often require compact, lightweight, and uniquely shaped electronic solutions that flexible PCBs can provide.
5. Is it possible to repair a flexible PCB?
Repairing flexible PCBs can be challenging due to their thin and flexible nature. While minor repairs are possible in some cases, it often requires specialized equipment and expertise. In many situations, especially with mass-produced consumer electronics, it may be more practical to replace the entire flexible PCB rather than attempt a repair.