Introduction
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) have revolutionized the lighting industry, offering energy-efficient and long-lasting solutions for various applications. As technology advances, different types of LED configurations have emerged to cater to specific needs and preferences. This article will explore three popular options for LED PCBs: Surface Mount Device (SMD) LEDs, Chip on Board (COB) LEDs, and Direct on Board (DOB) LEDs. We’ll delve into their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and applications to help you make an informed decision for your lighting projects.
Understanding LED PCBs
Before we dive into the specifics of SMD, COB, and DOB LEDs, it’s essential to understand the role of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) in LED technology. PCBs serve as the foundation for mounting and connecting electronic components, including LEDs. They provide mechanical support, electrical connections, and heat dissipation, which are crucial for the performance and longevity of LED systems.
SMD LED: Surface Mount Device
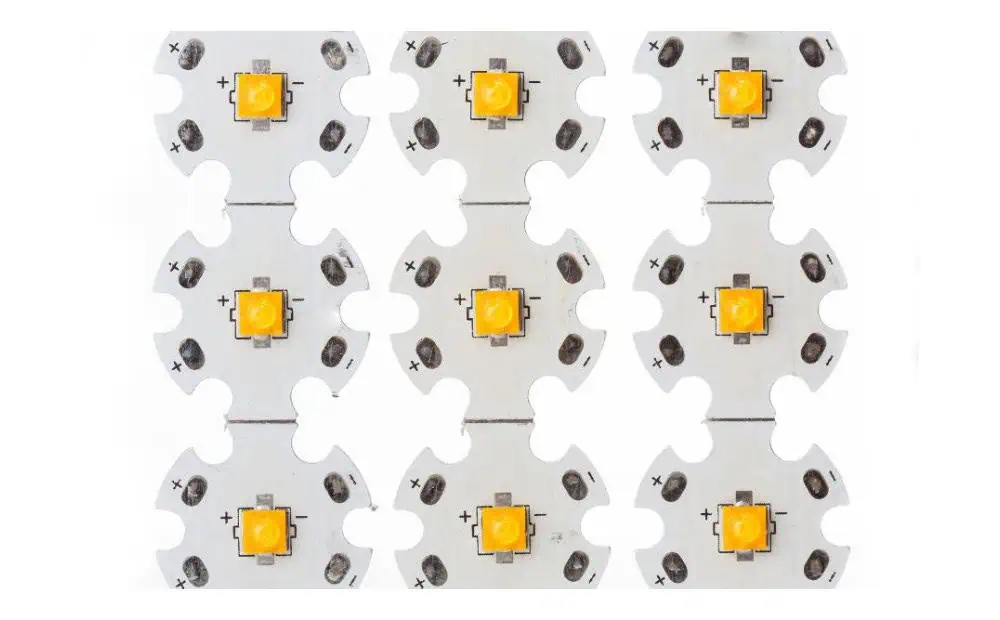
What is SMD LED?
Surface Mount Device (SMD) LEDs are compact, pre-packaged LED chips that can be directly mounted onto the surface of a PCB. They are widely used in various lighting applications due to their versatility and ease of integration.
Characteristics of SMD LEDs
- Size and Package: SMD LEDs come in various package sizes, typically ranging from 2835 (2.8mm x 3.5mm) to 5050 (5.0mm x 5.0mm).
- Components: Each SMD LED package contains one or more LED chips, a reflector cup, and wire bonding.
- Color Options: Available in a wide range of colors, including white, RGB, and multi-color configurations.
- Luminous Efficacy: Typically ranges from 100 to 160 lumens per watt, depending on the specific model and manufacturer.
Advantages of SMD LEDs
- Versatility: Can be used in various applications, from small electronics to large-scale lighting projects.
- Color Mixing: Easy to create multi-color or tunable white light solutions.
- Heat Dissipation: Generally good heat dissipation due to the spread-out nature of individual LEDs.
- Customization: Allows for flexible design and customization of light output and distribution.
Disadvantages of SMD LEDs
- Individual Mounting: Each LED must be individually placed on the PCB, which can be time-consuming for large-scale production.
- Potential for Non-Uniform Light: If not properly designed, may result in visible individual light sources or hot spots.
- More Components: Requires more components compared to COB or DOB LEDs, potentially increasing the risk of failure points.
Applications of SMD LEDs
- LED strips and tape lights
- Backlighting for displays and signage
- Automotive lighting
- General indoor and outdoor lighting fixtures
COB LED: Chip on Board
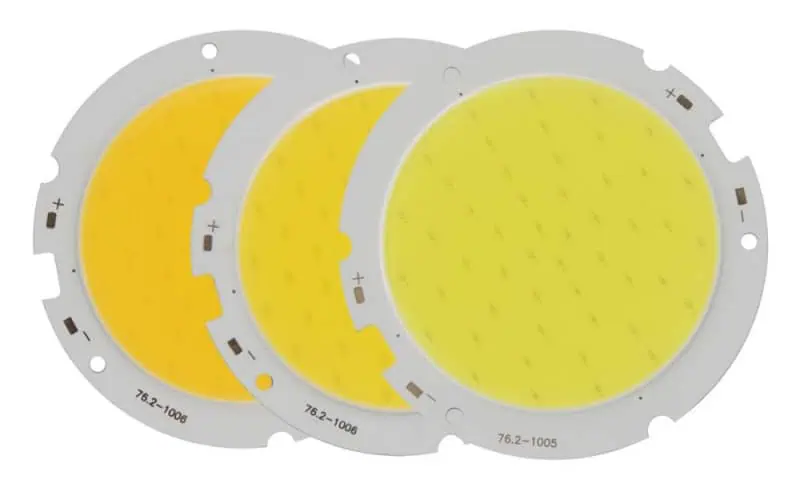

What is COB LED?
Chip on Board (COB) LED technology involves mounting multiple LED chips directly onto a substrate to form a single module. This results in a more compact and powerful light source compared to individual SMD LEDs.
Characteristics of COB LEDs
- Size and Package: COB LEDs are typically larger than SMD LEDs, with sizes ranging from 9mm to 30mm or more.
- Components: Multiple LED chips are mounted directly on a substrate and covered with a layer of phosphor (for white light).
- Color Options: Primarily available in white light with various color temperatures, though RGB options exist.
- Luminous Efficacy: Generally higher than SMD LEDs, ranging from 130 to 200 lumens per watt.
Advantages of COB LEDs
- High Lumen Density: Produces a large amount of light from a small area.
- Uniform Light Output: Creates a more even light distribution without visible individual light sources.
- Improved Thermal Management: Better heat dissipation due to direct mounting on the substrate.
- Simplified Manufacturing: Easier to assemble and requires fewer components than multiple SMD LEDs.
Disadvantages of COB LEDs
- Limited Color Options: Primarily available in white light, with fewer multi-color options compared to SMD LEDs.
- Less Flexibility in Design: The fixed nature of the COB module limits customization options.
- Higher Initial Cost: Generally more expensive per unit compared to SMD LEDs.
- Potential for Glare: The high lumen density can cause glare if not properly diffused or directed.
Applications of COB LEDs
- High-bay lighting for warehouses and industrial spaces
- Spotlights and track lighting
- Street and area lighting
- Automotive headlights
DOB LED: Direct on Board
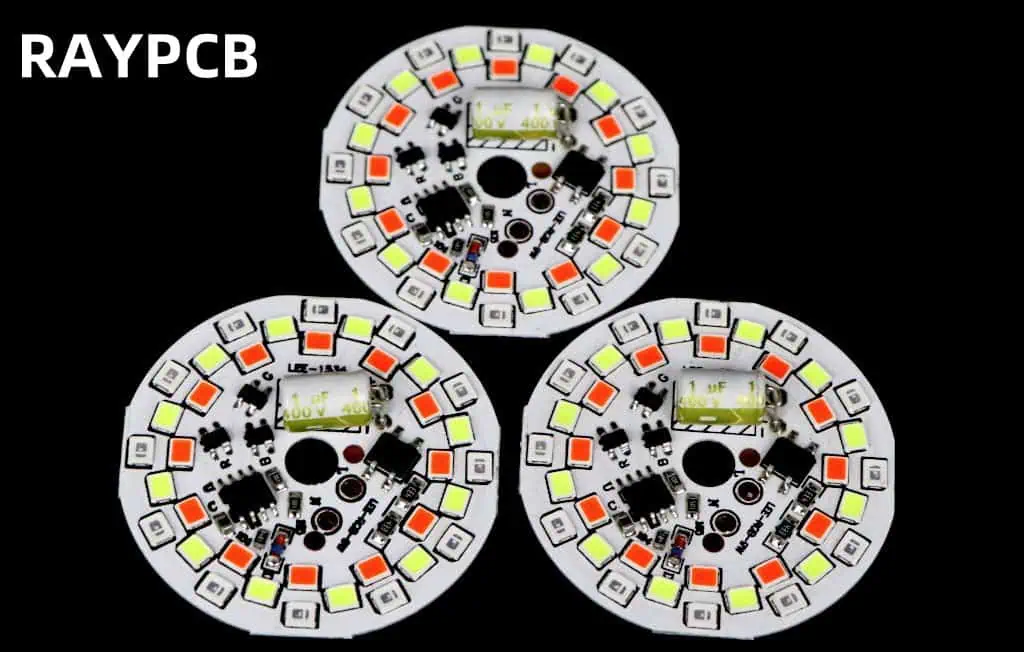

What is DOB LED?
Direct on Board (DOB) LED technology is the latest innovation in LED lighting. It involves mounting LED chips directly onto the main PCB without the need for a separate substrate or package.
Characteristics of DOB LEDs
- Size and Package: DOB LEDs are integrated directly into the PCB, allowing for very thin and compact designs.
- Components: LED chips are mounted directly on the main PCB along with other necessary components.
- Color Options: Available in various color temperatures of white light, with some RGB options.
- Luminous Efficacy: Comparable to or slightly higher than COB LEDs, ranging from 150 to 220 lumens per watt.
Advantages of DOB LEDs
- Simplified Manufacturing: Eliminates the need for a separate LED package or module, streamlining production.
- Improved Thermal Performance: Direct contact with the PCB allows for better heat dissipation.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces overall production costs by eliminating intermediate components and assembly steps.
- Ultra-Thin Designs: Enables the creation of extremely thin and lightweight lighting fixtures.
Disadvantages of DOB LEDs
- Limited Availability: As a newer technology, there may be fewer suppliers and options compared to SMD or COB LEDs.
- Specialized Equipment: May require specialized manufacturing equipment and processes.
- Repair Challenges: In case of LED failure, the entire PCB may need to be replaced.
- Design Constraints: The integration of LEDs directly on the PCB may limit some design flexibility.
Applications of DOB LEDs
- Flat panel lights
- Ultra-thin downlights
- Linear lighting fixtures
- Automotive interior lighting
Comparison of SMD, COB, and DOB LEDs
To better understand the differences between these three LED PCB options, let’s compare them across various parameters:
| Parameter | SMD LED | COB LED | DOB LED |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Small, individual packages | Larger, single module | Integrated into PCB |
| Lumen Density | Moderate | High | High |
| Color Options | Wide range, including RGB | Primarily white, limited RGB | Primarily white, some RGB |
| Heat Dissipation | Good | Better | Best |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Moderate | Low | Lowest |
| Customization | High | Limited | Moderate |
| Luminous Efficacy (lm/W) | 100-160 | 130-200 | 150-220 |
| Glare Potential | Low | High | Moderate |
| Repair/Replacement | Easy | Moderate | Difficult |
Choosing the Right LED PCB Option
When selecting between SMD, COB, and DOB LEDs for your project, consider the following factors:
- Application: Determine the specific lighting requirements for your project.
- Light Output: Consider the desired lumen output and distribution pattern.
- Color Requirements: Decide if you need white light, specific color temperatures, or RGB capabilities.
- Space Constraints: Evaluate the available space for the lighting fixture.
- Thermal Management: Assess the heat dissipation needs of your application.
- Cost Considerations: Balance initial costs with long-term energy efficiency and maintenance.
- Manufacturing Capabilities: Consider your production volume and available manufacturing processes.
Application-Specific Recommendations
| Application | Recommended LED Type | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| LED Strips | SMD LED | Flexibility and color options |
| High-Bay Lighting | COB LED | High lumen output and uniform distribution |
| Ultra-Thin Panels | DOB LED | Compact design and efficient heat management |
| Automotive Lighting | SMD or COB LED | Versatility for different automotive applications |
| Outdoor Lighting | COB or DOB LED | High efficiency and good thermal management |
| Decorative Lighting | SMD LED | Wide color range and design flexibility |
Future Trends in LED PCB Technology
As LED technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see further improvements in efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and application-specific solutions. Some potential trends include:
- Increased DOB LED Adoption: As manufacturing processes improve, DOB LEDs may become more prevalent across various lighting applications.
- Hybrid Solutions: Combinations of different LED types on a single PCB to optimize performance for specific use cases.
- Advanced Thermal Management: Development of new materials and designs to further improve heat dissipation.
- Smart Integration: Incorporation of sensors and control systems directly into LED PCBs for improved functionality and energy efficiency.
- Micro-LED Technology: Advancements in extremely small LED chips may lead to new possibilities in display and lighting applications.
Conclusion
SMD, COB, and DOB LEDs each offer unique advantages and are suited for different applications in the world of lighting. SMD LEDs provide versatility and color options, COB LEDs offer high lumen density and uniform output, while DOB LEDs excel in thermal management and manufacturing simplicity. By understanding the characteristics, pros, and cons of each option, you can make an informed decision for your specific lighting project. As LED technology continues to advance, we can expect even more efficient and innovative solutions to emerge, further revolutionizing the lighting industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Which LED type is best for energy efficiency?
While all three types are energy-efficient, DOB LEDs generally offer the highest luminous efficacy, followed closely by COB LEDs. However, the overall energy efficiency of a lighting system depends on various factors, including the specific product, driver efficiency, and thermal management.
2. Can I replace SMD LEDs with COB or DOB LEDs in existing fixtures?
In most cases, it’s not a straightforward replacement due to differences in size, power requirements, and heat dissipation. It’s usually best to design fixtures specifically for the chosen LED type. However, some modular systems may allow for easier upgrades or replacements.
3. Are COB LEDs always better than SMD LEDs for high-power applications?
While COB LEDs are often preferred for high-power applications due to their high lumen density and better thermal management, SMD LEDs can still be suitable in some cases. The choice depends on factors such as the specific power requirements, desired beam angle, and color mixing needs.
4. How do I determine which LED type is best for my project?
Consider factors such as the required light output, color options, space constraints, thermal management needs, and budget. It’s often helpful to consult with lighting designers or engineers who can provide expertise based on your specific project requirements.
5. Are DOB LEDs more expensive than SMD or COB LEDs?
Initially, DOB LEDs may have a higher cost due to the newer technology and potentially specialized manufacturing processes. However, they can be more cost-effective in the long run due to simplified manufacturing, improved thermal management, and potentially longer lifespans. As the technology becomes more widespread, costs are likely to decrease.