In recent years, the LED industry has experienced exponential growth, revolutionizing lighting technology across various sectors. As LEDs become more powerful and efficient, the need for effective thermal management has become increasingly critical. This is where Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs) play a crucial role. MCPCBs have emerged as an essential component in LED manufacturing, offering superior heat dissipation properties that significantly enhance the performance and longevity of LED products.
This comprehensive article will explore the vital role of MCPCBs in the LED industry, delving into their structure, benefits, applications, and impact on LED technology advancements.
Understanding MCPCBs
What is an MCPCB?
A Metal Core Printed Circuit Board (MCPCB), also known as an Insulated Metal Substrate (IMS), is a specialized type of printed circuit board designed to efficiently transfer heat away from electronic components. Unlike traditional FR-4 PCBs, MCPCBs feature a metal base layer that serves as an excellent heat conductor.
Structure of MCPCBs
MCPCBs typically consist of three main layers:
- Metal Base Layer
- Dielectric Layer
- Circuit Layer
Let’s examine each layer in detail:
Metal Base Layer
The metal base forms the foundation of the MCPCB and is responsible for its superior heat dissipation capabilities.
| Common Materials | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Advantages |
| Aluminum | 150-200 | Cost-effective, lightweight |
| Copper | 380-400 | Excellent thermal conductivity |
| Copper-Molybdenum-Copper | 200-300 | Tailored coefficient of thermal expansion |
Dielectric Layer
This thin insulating layer electrically isolates the circuit layer from the metal base while facilitating heat transfer.
| Property | Typical Range | Importance |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1-7 W/m·K | Higher values improve heat transfer |
| Breakdown Voltage | 1500-3000 V/mil | Ensures electrical isolation |
| Thickness | 50-100 碌m | Balances insulation and heat transfer |
Circuit Layer
The topmost layer where the electrical circuits and components are mounted, typically made of copper.
| Aspect | Specification | Purpose |
| Copper Thickness | 1-10 oz | Determines current carrying capacity |
| Surface Finish | ENIG, HASL, OSP, etc. | Protects copper and enhances solderability |
Advantages of MCPCBs in LED Applications
Enhanced Thermal Management
The primary advantage of MCPCBs in LED applications is their superior heat dissipation capabilities.
Comparative Heat Dissipation
| PCB Type | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
| Standard FR-4 | 0.2-0.3 |
| High-Tg FR-4 | 0.3-0.5 |
| Aluminum MCPCB | 1.0-3.0 |
| Copper MCPCB | 2.0-4.0 |
Improved LED Performance
Efficient heat dissipation leads to several performance benefits:
- Increased Luminous Efficacy
- Extended Lifespan
- Color Stability
- Higher Power Density
Cost-Effectiveness
While MCPCBs have a higher initial cost compared to traditional FR-4 PCBs, they offer long-term cost savings:
- Reduced need for additional heat sinks
- Lower failure rates and replacement costs
- Improved energy efficiency
Design Flexibility
MCPCBs offer various design options to suit different LED applications:
| Design Aspect | Options | Benefits |
| Shape | Round, rectangular, custom | Fits various product designs |
| Thickness | 0.5mm to 3mm+ | Balances heat dissipation and weight |
| Surface Finish | White solder mask, black solder mask | Enhances reflectivity or aesthetics |
Applications of MCPCBs in the LED Industry
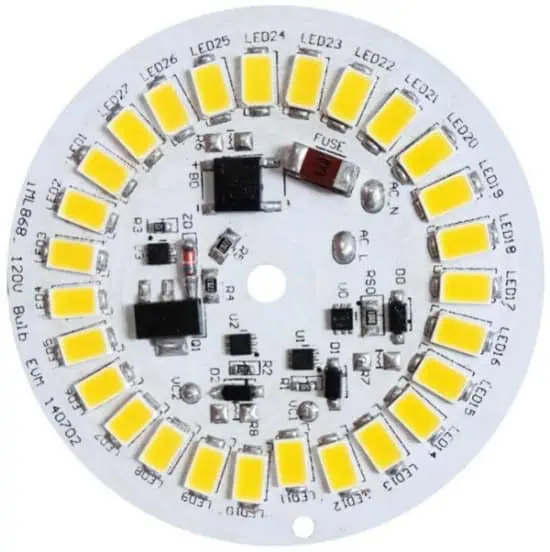
High-Power LED Lighting
MCPCBs are essential for high-power LED applications where thermal management is critical.
Examples of High-Power LED Applications
- Street Lighting
- Industrial Lighting
- Automotive Headlights
- Stadium Lighting
LED Displays and Signage
Large-scale LED displays and digital signage benefit from the thermal management properties of MCPCBs.
| Application | Benefits of MCPCBs |
| Outdoor LED Billboards | Withstands environmental stress, maintains brightness |
| Indoor Video Walls | Enables higher pixel density, uniform illumination |
| Traffic Signals | Enhances reliability, reduces maintenance |
Automotive LED Lighting
The automotive industry increasingly relies on LED lighting for both functional and aesthetic purposes.
Automotive LED Applications using MCPCBs
- Headlights and Taillights
- Dashboard Illumination
- Interior Ambient Lighting
- Daytime Running Lights (DRLs)
Consumer Electronics
MCPCBs are finding their way into various consumer electronic devices that incorporate LED technology.
| Device Category | LED Application | MCPCB Advantage |
| Smartphones | Flash LEDs, Display Backlighting | Compact design, efficient cooling |
| Televisions | LED Backlighting | Uniform light distribution, longevity |
| Computer Monitors | Edge-lit LEDs | Slim profile, enhanced brightness |
Horticultural Lighting
The growing indoor farming industry relies heavily on LED lighting, where MCPCBs play a crucial role.
- Enables high-intensity lighting for plant growth
- Allows for customized spectrum control
- Improves energy efficiency in controlled environment agriculture
Manufacturing Processes for MCPCBs
Base Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with the selection and preparation of the metal core material.
- Metal sheet cutting and cleaning
- Surface treatment for improved adhesion
Dielectric Layer Application
The dielectric layer is crucial for the MCPCB’s performance.
| Method | Description | Advantages |
| Prepreg Lamination | Heat and pressure bond prepreg to metal | Consistent thickness, good adhesion |
| Direct Coating | Liquid dielectric applied and cured | Thinner layers possible, cost-effective |
Circuit Layer Formation
The circuit layer is typically formed through one of two methods:
- Subtractive Process (Etching)
- Additive Process (Plating)
Surface Finish Application
Various surface finishes can be applied to enhance solderability and protect the copper layer.
| Finish Type | Characteristics | Best For |
| ENIG | Flat surface, good solderability | Fine-pitch components |
| HASL | Cost-effective, durable | General-purpose applications |
| OSP | Thin organic coating, environmentally friendly | Short shelf-life products |
Quality Control and Testing
Rigorous testing ensures the reliability and performance of MCPCBs:
- Thermal conductivity testing
- Dielectric strength testing
- Peel strength testing
- Thermal cycling tests
Challenges and Future Trends
Current Challenges in MCPCB Technology
- Cost Reduction: Balancing performance with affordability
- Thermal Management for Ultra-High-Power LEDs
- Miniaturization: Maintaining thermal performance in smaller form factors
- Environmental Concerns: Developing more sustainable manufacturing processes
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Advanced Materials

Research into new materials aims to enhance thermal performance further:
| Material | Potential Advantage |
| Graphene-enhanced dielectrics | Significantly higher thermal conductivity |
| Ceramic-metal composites | Tailored thermal expansion, improved durability |
| Nano-particle filled polymers | Enhanced thermal conductivity, reduced weight |
Intelligent Thermal Management
Integration of smart technologies for active thermal management:
- Embedded temperature sensors
- Microcontroller-based thermal regulation
- IoT-enabled thermal monitoring and control
3D Printing of MCPCBs
Additive manufacturing techniques show promise for creating complex MCPCB designs:
- Customized thermal paths
- Reduced material waste
- Rapid prototyping capabilities
Hybrid PCB Technologies
Combining MCPCB technology with other PCB types for optimized performance:
- MCPCB and flexible PCB hybrids for wearable LED devices
- Rigid-flex MCPCBs for automotive applications
The Impact of MCPCBs on LED Industry Advancements
Enabling Higher Brightness LEDs
MCPCBs have been instrumental in the development of increasingly powerful LEDs:
| Year | Typical LED Brightness (lumens/watt) | MCPCB Role |
| 2000 | 20-30 | Limited use of MCPCBs |
| 2010 | 70-100 | Widespread adoption of aluminum MCPCBs |
| 2020 | 150-200 | Advanced MCPCB materials and designs |
| 2030 (projected) | 250-300 | Next-gen MCPCBs with novel materials |
Improving Energy Efficiency
The superior thermal management of MCPCBs contributes to overall energy efficiency improvements in LED lighting systems:
- Reduced energy loss as heat
- Maintenance of LED efficiency at higher operating temperatures
- Enabling more compact, efficient lighting designs
Expanding LED Applications
MCPCBs have facilitated the expansion of LED technology into new applications:
- High-power projectors and entertainment lighting
- UV LEDs for disinfection and curing processes
- Infrared LEDs for night vision and sensing applications
- Micro-LED displays for augmented and virtual reality devices
Enhancing LED Reliability and Lifespan
The use of MCPCBs significantly impacts the reliability and lifespan of LED products:
| Aspect | Without MCPCB | With MCPCB |
| Typical Lifespan | 30,000-50,000 hours | 50,000-100,000+ hours |
| Lumen Maintenance | 70% at 30,000 hours | 70% at 50,000+ hours |
| Failure Rate | Higher due to thermal stress | Significantly reduced |
Conclusion
Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs) have become an indispensable component in the LED industry, driving innovation and enabling the development of higher-performance, more reliable LED products. Their superior thermal management capabilities have allowed LEDs to push the boundaries of brightness, efficiency, and application diversity.
As the LED industry continues to evolve, MCPCBs will play an increasingly crucial role in addressing the thermal challenges associated with next-generation LED technologies. The ongoing research into advanced materials and manufacturing techniques promises to further enhance the capabilities of MCPCBs, paving the way for even more exciting developments in LED technology.
The symbiotic relationship between MCPCB technology and LED advancements will undoubtedly continue to shape the future of lighting, displays, and numerous other applications, driving us towards a brighter, more energy-efficient future.
FAQ
Q1: Are MCPCBs only used for LED applications?
A1: While MCPCBs are predominantly used in the LED industry due to their excellent thermal management properties, they are not limited to LED applications. MCPCBs are also used in other high-power electronics applications where heat dissipation is critical, such as power supplies, motor drives, and radio frequency (RF) devices. However, their widespread adoption and continuous development have been primarily driven by the LED industry’s demands.
Q2: How do MCPCBs compare to ceramic PCBs for LED applications?
A2: Both MCPCBs and ceramic PCBs offer excellent thermal management for LED applications, but they have different characteristics:
| Aspect | MCPCBs | Ceramic PCBs |
| Thermal Conductivity | Good (1-3 W/m·K) | Excellent (20-170+ W/m·K) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Manufacturability | Easier, more widely available | More challenging, specialized |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | Brittle, can be fragile |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
Ceramic PCBs generally offer superior thermal performance but at a higher cost and with some manufacturing limitations. MCPCBs provide a good balance of performance, cost, and ease of manufacturing, making them the preferred choice for many LED applications.
Q3: Can MCPCBs be recycled?
A3: Yes, MCPCBs can be recycled, but the process is more complex than recycling standard FR-4 PCBs due to their multi-layer structure. The recycling process typically involves:
- Mechanical separation of components
- Shredding or grinding of the MCPCB
- Separation of metals (usually aluminum or copper) from the dielectric material
- Refining and reuse of the metal content
The metal content, particularly aluminum, makes MCPCBs attractive for recycling. However, the dielectric layer can pose challenges in the recycling process. As environmental concerns grow, research is ongoing to develop more easily recyclable MCPCB materials and improve recycling techniques.
Q4: How do I choose the right MCPCB for my LED application?
A4: Selecting the appropriate MCPCB for your LED application involves considering several factors:
- Thermal requirements: Calculate the heat generated by your LEDs and choose an MCPCB with suitable thermal conductivity.
- Electrical requirements: Consider voltage isolation, current carrying capacity, and circuit complexity.
- Environmental conditions: Factor in operating temperature range, humidity, and exposure to elements.
- Mechanical requirements: Consider size constraints, mounting options, and any required certifications.
- Cost considerations: Balance performance needs with budget constraints.
It’s often beneficial to work with MCPCB manufacturers or thermal management experts to ensure the optimal selection for your specific application.
Q5: What are the limitations of MCPCBs in LED applications?
A5: While MCPCBs offer significant advantages for LED applications, they do have some limitations:
- Cost: MCPCBs are generally more expensive than standard FR-4 PCBs, which can impact overall product cost.
- Design complexity: The metal core can limit the ability to create multi-layer designs, potentially restricting circuit complexity.
- Weight: MCPCBs are heavier than FR-4 PCBs, which may be a concern in weight-sensitive applications.
- Thermal expansion mismatch: The difference in thermal expansion between the metal core and other components can cause stress in some designs.
- Limited flexibility: MCPCBs are rigid, making them unsuitable for applications requiring flexible or bendable PCBs.
Despite these limitations, the benefits of MCPCBs often outweigh the drawbacks in many LED applications, particularly those involving high-power LEDs or where thermal management is critical.
