In the world of electronics manufacturing, ensuring the quality and reliability of printed circuit board assemblies (PCBAs) is paramount. Functional testing plays a crucial role in this process, verifying that each PCBA operates as intended before it reaches the end-user. This article delves into the intricacies of functional testing for PCB assemblies, exploring various testing methods, their importance, and the associated costs. We’ll also examine how these costs can impact overall production and ways to optimize the testing process for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Understanding Functional Testing in PCBA
What is Functional Testing?
Functional testing, also known as Functional Circuit Testing (FCT), is a critical step in the PCBA manufacturing process. It involves powering up the assembled PCB and testing its functionality to ensure it performs according to design specifications.
Importance of Functional Testing
Quality Assurance
Functional testing serves as the final quality check before a PCBA is shipped or integrated into a larger system.
Defect Detection
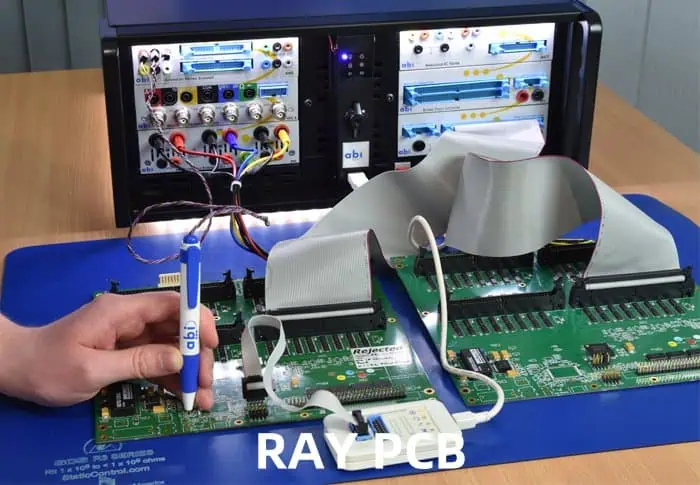

It helps identify issues that may not be apparent through visual inspection or other testing methods.
Performance Verification
FCT confirms that the PCBA meets the required performance standards and specifications.
Types of Functional Tests
| Test Type | Description | Typical Applications |
| Power-On Test | Verifies basic power supply functionality | All PCBAs |
| Signal Integrity Test | Checks signal quality and timing | High-speed digital circuits |
| Communication Interface Test | Validates various communication protocols | PCBAs with network capabilities |
| Sensor and Actuator Test | Verifies functionality of input/output devices | IoT devices, automotive electronics |
| Environmental Stress Test | Checks performance under various environmental conditions | Military, aerospace a |
Functional Testing Process
Pre-Test Preparation
- Developing test plans and procedures
- Creating test fixtures and programming test equipment
- Calibrating test instruments
Test Execution
Manual Testing
Involves human operators performing tests using various instruments and following predefined procedures.
Automated Testing
Utilizes computerized test equipment and software to perform a series of predefined tests automatically.
Post-Test Analysis
- Data collection and analysis
- Defect categorization
- Reporting and documentation
Factors Affecting PCBA FCT Costs
Test Equipment Costs
Automated Test Equipment (ATE)
High-end ATE systems can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars but offer faster and more consistent testing.
Specialized Instruments
Oscilloscopes, multimeters, and other specialized testing instruments contribute to overall equipment costs.
Test Fixture Costs
Custom fixtures designed for specific PCBAs can be a significant expense, especially for complex or unique designs.
Labor Costs
| Testing Approach | Labor Intensity | Skill Level Required |
| Manual Testing | High | Medium to High |
| Semi-Automated Testing | Medium | Medium |
| Fully Automated Testing | Low | High (for setup and maintenance) |
Test Development Costs
- Test plan creation
- Test software development
- Fixture design and fabrication
Production Volume Impact
| Production Volume | Cost per Unit | Initial Setup Cost |
| Low Volume | Higher | Lower |
| High Volume | Lower | Higher |
Complexity of PCBA
More complex PCBAs with numerous components and functions typically require more extensive and costly testing procedures.
Strategies for Optimizing FCT Costs

Design for Testability (DFT)
Implementing DFT principles during the PCB design phase can significantly reduce testing complexity and costs.
Key DFT Practices
- Including test points and access pads
- Designing modular circuits
- Implementing self-test features
Test Coverage Optimization
Balancing test coverage with testing time and costs to achieve optimal quality assurance.
Automation Implementation
While initially costly, automating the testing process can lead to long-term cost savings, especially for high-volume production.
In-Circuit Test (ICT) vs. Functional Test Trade-offs
| Test Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| In-Circuit Test | Faster, better fault isolation | Higher fixture costs, limited functional testing |
| Functional Test | Comprehensive performance verification | Longer test times, more complex setup |
Combining ICT and FCT can often provide a cost-effective solution with comprehensive test coverage.
Standardization and Reusability
Developing standardized test procedures and reusable test fixtures can reduce costs across multiple projects.
Emerging Trends in PCBA Functional Testing
Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing
Integration of FCT data with manufacturing execution systems (MES) for real-time quality control and process optimization.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Using AI/ML algorithms to:
- Predict potential defects
- Optimize test sequences
- Analyze test data for continuous improvement
Virtual and Augmented Reality in Testing
VR/AR technologies can assist in:
- Test operator training
- Guided testing procedures
- Remote troubleshooting
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Functional Testing
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Costs
| Aspect | Short-Term Impact | Long-Term Impact |
| Equipment Investment | High initial cost | Reduced per-unit testing cost |
| Quality Improvement | Immediate defect reduction | Enhanced brand reputation, fewer returns |
| Process Optimization | Initial disruption | Increased efficiency and throughput |
ROI Calculation
Factors to consider in Return on Investment (ROI) calculation:
- Reduction in field failures and warranty claims
- Increased production yield
- Reduced rework and scrap costs
- Improved customer satisfaction and retention
Case Studies: FCT Implementation and Cost Analysis
Case Study 1: High-Volume Consumer Electronics
A smartphone manufacturer implemented automated FCT, resulting in:
- 30% reduction in overall testing time
- 50% decrease in field failure rates
- 20% increase in production yield
Initial investment was recouped within 18 months.
Case Study 2: Low-Volume, High-Complexity Aerospace PCBAs
An aerospace company optimized its FCT process for low-volume, high-complexity PCBAs:
- Developed modular test fixtures
- Implemented AI-assisted test sequence optimization
- Achieved 40% reduction in test development time
- Improved fault detection rate by 25%
Future of PCBA Functional Testing
5G and High-Speed Circuit Testing
As 5G technology becomes more prevalent, new testing methodologies for high-speed circuits will be required.
IoT and Edge Computing Challenges
The proliferation of IoT devices will necessitate more sophisticated and efficient testing procedures to handle diverse functionality and connectivity options.
Sustainability in Testing
Growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices will drive the development of more energy-efficient testing methods and equipment.
Conclusion
Functional testing of PCB assemblies is a critical process that ensures the quality and reliability of electronic products. While it represents a significant cost in the manufacturing process, the benefits of comprehensive FCT far outweigh the expenses when considering long-term product reliability and customer satisfaction.
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the methods and tools used in PCBA functional testing. Manufacturers who invest in optimizing their testing processes and embrace new technologies stand to gain a competitive edge in terms of both product quality and production efficiency.
The key to successful and cost-effective functional testing lies in finding the right balance between test coverage, automation, and adaptability to changing technological landscapes. By carefully considering the factors affecting FCT costs and implementing strategies to optimize the testing process, manufacturers can ensure high-quality PCBAs while managing production costs effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How long does functional testing typically take for a PCBA?
The duration of functional testing can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the PCBA and the extent of testing required. For simple PCBAs, functional testing might take only a few minutes per board. However, for complex PCBAs or those requiring extensive environmental testing, the process could take hours or even days. On average, functional testing for a moderately complex PCBA might take anywhere from 5 to 30 minutes per board.
2. Can functional testing detect all possible defects in a PCBA?
While functional testing is comprehensive, it cannot guarantee the detection of all possible defects. It is excellent at identifying operational issues and verifying that the PCBA functions as intended under normal conditions. However, some latent defects or issues that only manifest under specific circumstances might not be detected. This is why functional testing is often used in conjunction with other testing methods like in-circuit testing, visual inspection, and environmental stress testing for more complete coverage.
3. How does the cost of functional testing compare to other testing methods?
The cost of functional testing generally falls between in-circuit testing (ICT) and visual inspection in terms of per-unit cost. Here’s a rough comparison:
| Testing Method | Relative Cost | Test Coverage |
| Visual Inspection | Low | Limited |
| In-Circuit Testing | Medium-High | Good for component-level defects |
| Functional Testing | Medium | Excellent for operational verification |
| Burn-in Testing | High | Best for reliability issues |
The actual costs can vary significantly based on production volume, PCBA complexity, and specific testing requirements.
4. Is it possible to reduce functional testing costs without compromising quality?
Yes, there are several strategies to reduce functional testing costs while maintaining quality:
- Implement Design for Testability (DFT) principles
- Optimize test coverage to focus on critical functions
- Automate testing processes where possible
- Develop reusable test fixtures and procedures
- Combine functional testing with other testing methods strategically
- Continuously analyze and improve the testing process
The key is to focus on efficiency and effectiveness rather than simply cutting corners.
5. How often should functional test equipment and procedures be updated?
Functional test equipment and procedures should be reviewed and potentially updated:
- When new product designs are introduced
- If there are significant changes in manufacturing processes
- When new technologies or testing methodologies become available
- If there’s an increase in field failures or quality issues
- At regular intervals (e.g., annually) as part of continuous improvement efforts
Regular updates ensure that the testing process remains effective, efficient, and aligned with current technological standards and product requirements.
