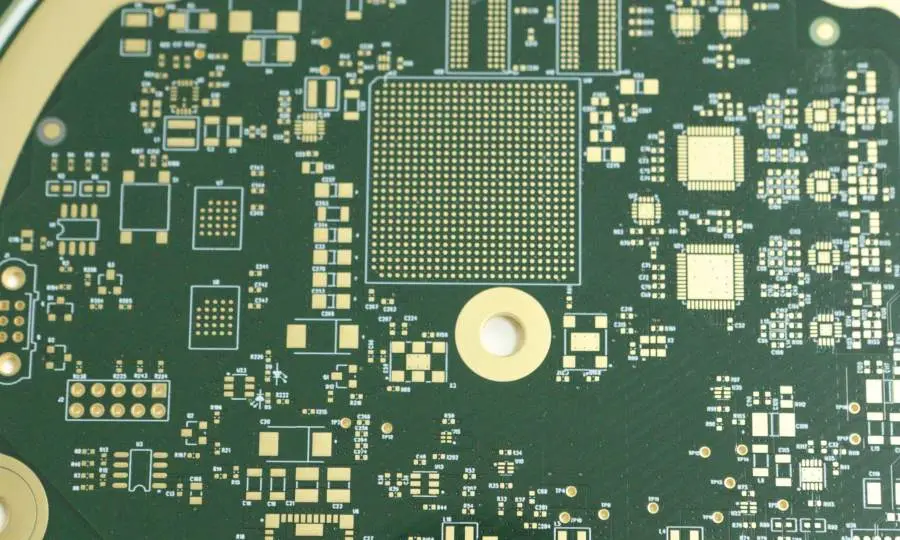
What is ENIG PCB? Complete Guide to Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold
ENIG (Electroless nickel immersion gold) is a dual-layer metallic coating consisting of a thin gold layer deposited over an underlying nickel layer.
Introduction
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) require surface finishes that provide excellent solderability, corrosion resistance, and long-term reliability. Among the various surface finish options available, Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG) has emerged as one of the most popular and versatile choices for modern PCB applications. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about ENIG PCBs, from their fundamental principles to practical applications and manufacturing considerations.
ENIG represents a sophisticated surface finishing technology that combines the protective properties of nickel with the superior conductivity and oxidation resistance of gold. This dual-layer approach has revolutionized PCB manufacturing, enabling the production of highly reliable electronic devices across industries ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace applications.
What is ENIG PCB?
ENIG stands for Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold, a surface finish applied to printed circuit boards to protect copper traces and provide excellent solderability. Unlike traditional electroplating processes that require electrical current, ENIG utilizes chemical reactions to deposit both nickel and gold layers onto copper surfaces.
The ENIG finish consists of two distinct metallic layers:
- Nickel Layer: Typically 3-6 micrometers thick, serving as a barrier between copper and gold
- Gold Layer: Usually 0.05-0.23 micrometers thick, providing oxidation protection and solderability
This combination creates a robust, reliable surface that maintains its properties over extended periods, making it ideal for high-performance electronic applications.
ENIG PCB We Served

1u” ENIG PCB
2u” ENIG PCB
3u” ENIG PCB

4u” ENIG PCB
The ENIG Process: How It Works
Chemical Process Overview
The ENIG process involves several carefully controlled chemical steps that must be executed with precision to achieve optimal results:
1. Substrate Preparation The PCB substrate undergoes thorough cleaning to remove any contamination, oxidation, or residues that could interfere with the plating process. This typically involves:
- Alkaline cleaning to remove organic contaminants
- Micro-etching to create an optimal surface texture
- Acid cleaning to remove any remaining oxides
2. Electroless Nickel Deposition The cleaned PCB is immersed in an electroless nickel plating solution containing:
- Nickel sulfate or nickel chloride as the nickel source
- Sodium hypophosphite as the reducing agent
- Various stabilizers and pH controllers
The chemical reaction deposits a uniform nickel-phosphorus alloy layer across all exposed copper surfaces, regardless of geometry complexity.
3. Immersion Gold Deposition Following nickel deposition, the PCB enters an immersion gold bath where:
- Gold displaces a thin layer of the nickel surface
- The process is self-limiting, creating a consistent gold thickness
- The gold layer forms through a displacement reaction without external current
4. Final Processing The finished PCBs undergo final cleaning and inspection to ensure quality standards are met.
Key Chemical Reactions
The electroless nickel deposition follows this primary reaction:
Ni²⁺ + H₂PO₂⁻ + H₂O → Ni + H₂PO₃⁻ + 2H⁺The immersion gold process involves:
Ni + 2Au³⁺ → Ni²⁺ + 2AuStructure and Composition
Layer Composition
Nickel Layer Characteristics:
- Composition: Nickel-phosphorus alloy (typically 7-12% phosphorus)
- Thickness: 3-6 micrometers (120-240 microinches)
- Structure: Amorphous when deposited, can crystallize when heated
- Properties: Excellent barrier protection, good solderability
Gold Layer Characteristics:
- Composition: Nearly pure gold (99.9%+)
- Thickness: 0.05-0.23 micrometers (2-9 microinches)
- Structure: Crystalline, thin, and uniform
- Properties: Superior corrosion resistance, excellent electrical conductivity
Interface Properties
The interface between nickel and gold forms through a controlled displacement reaction that creates excellent adhesion. The thin gold layer allows for effective solder wetting while the nickel barrier prevents copper migration and maintains long-term reliability.
Manufacturing Process Details
Process Parameters
Temperature Control:
- Electroless nickel: 85-95°C (185-203°F)
- Immersion gold: 85-95°C (185-203°F)
- Precise temperature control ensures consistent deposition rates
pH Management:
- Electroless nickel: pH 4.2-5.2
- Immersion gold: pH 4.5-5.5
- Automated pH control systems maintain optimal conditions
Solution Maintenance:
- Regular chemical analysis and replenishment
- Filtration to remove particulates
- Loading control to maintain consistent results
Quality Control Measures
Thickness Monitoring:
- X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy for accurate measurement
- Regular coupon testing for process verification
- Statistical process control to track trends
Surface Analysis:
- Microscopic examination for surface defects
- Solderability testing using standardized methods
- Adhesion testing to ensure proper layer bonding
Advantages of ENIG PCB
Superior Solderability
ENIG provides excellent solderability characteristics that remain stable over extended periods:
- Long-term stability: Gold surface resists oxidation indefinitely
- Multiple reflow capability: Can withstand multiple thermal cycles
- Lead-free compatibility: Excellent performance with lead-free solder alloys
- Fine-pitch applications: Suitable for small component pitches and BGA applications
Excellent Corrosion Resistance
The dual-layer structure provides comprehensive protection:
- Gold layer: Prevents oxidation of underlying metals
- Nickel barrier: Blocks copper migration and corrosion
- Chemical resistance: Withstands exposure to various chemicals and environments
- Humidity protection: Maintains performance in high-humidity conditions
Uniform Coverage
ENIG’s electroless and immersion processes ensure consistent coverage:
- Complex geometries: Reaches all areas regardless of shape or accessibility
- Uniform thickness: Chemical deposition provides consistent layer thickness
- Via coverage: Excellent coverage inside via holes and on vertical surfaces
- Edge coverage: Maintains protection at PCB edges and cut areas
Electrical Properties
ENIG offers superior electrical characteristics:
- Low contact resistance: Gold provides excellent electrical contact
- Signal integrity: Minimal impact on high-frequency signals
- Current carrying capacity: Suitable for power applications
- EMI shielding: Contributes to electromagnetic interference reduction
Disadvantages and Limitations
Cost Considerations
ENIG is generally more expensive than basic surface finishes:
- Material costs: Gold content increases raw material expenses
- Process complexity: Requires specialized equipment and expertise
- Waste treatment: Chemical disposal adds to operational costs
- Quality control: Extensive testing requirements increase overall costs
Technical Limitations
Black Pad Defect:
- Potential for nickel corrosion at the nickel-gold interface
- Can cause poor solder joint reliability
- Requires careful process control to prevent occurrence
- May necessitate specialized testing for detection
Phosphorus Content Issues:
- High phosphorus levels can affect solderability
- May cause brittleness in extreme cases
- Requires optimization based on specific applications
- Can influence thermal cycling performance
Thickness Variations:
- Achieving consistent thin gold layers can be challenging
- Over-plating increases costs unnecessarily
- Under-plating may compromise performance
- Requires precise process control and monitoring
Applications and Use Cases
Consumer Electronics
ENIG is widely used in consumer electronic devices:
- Smartphones and tablets: High-density interconnects and fine-pitch components
- Laptops and computers: Multi-layer boards with complex routing
- Gaming consoles: High-performance applications requiring reliability
- Wearable devices: Miniaturized circuits with space constraints
Automotive Electronics
The automotive industry relies heavily on ENIG for critical applications:
- Engine control modules: High-temperature and vibration resistance
- Safety systems: ABS, airbag controllers, and stability systems
- Infotainment systems: Complex multi-layer boards with high component density
- Electric vehicle components: Power electronics and battery management systems
Industrial and Medical Applications
ENIG meets the stringent requirements of industrial and medical electronics:
- Medical devices: Implantable devices and diagnostic equipment
- Industrial automation: PLCs, motor drives, and control systems
- Test and measurement: High-precision instruments requiring stable performance
- Aerospace and defense: Mission-critical applications with extreme reliability requirements
Telecommunications
Modern communication infrastructure depends on ENIG technology:
- Base stations: High-frequency RF applications
- Networking equipment: Routers, switches, and servers
- Fiber optic systems: High-speed data transmission equipment
- Satellite communications: Space-qualified electronics requiring long-term reliability
Comparison with Other Surface Finishes

ENIG vs. HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling)
Advantages of ENIG:
- Flat surface ideal for fine-pitch components
- No thermal stress during application
- Better shelf life and storage stability
- Superior performance with lead-free solders
Advantages of HASL:
- Lower cost
- Proven reliability in standard applications
- Self-fluxing properties
- Wide process window
ENIG vs. OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative)
Advantages of ENIG:
- Multiple reflow capability
- Better storage life
- Superior corrosion protection
- Suitable for press-fit applications
Advantages of OSP:
- Lowest cost option
- Environmentally friendly
- Flat surface finish
- Easy reworkability
ENIG vs. Immersion Silver
Advantages of ENIG:
- Better corrosion resistance
- Longer shelf life
- Superior wire bonding capability
- Better performance in harsh environments
Advantages of Immersion Silver:
- Lower cost than ENIG
- Excellent electrical properties
- Good thermal conductivity
- Suitable for high-frequency applications
Design Considerations for ENIG PCBs
Pad Design Guidelines
Size Recommendations:
- Minimum pad size: 0.1mm (4 mils) for reliable coverage
- Aspect ratio considerations for via fills
- Solder mask registration requirements
- Thermal relief design for large pads
Shape Optimization:
- Rounded corners to improve solder flow
- Appropriate solder mask expansion
- Via-in-pad considerations for BGA applications
- Land pattern optimization for different component types
Layout Considerations
Spacing Requirements:
- Minimum trace spacing based on ENIG thickness
- Consideration of manufacturing tolerances
- Via placement for optimal coverage
- Ground plane design for thermal management
Signal Integrity:
- Impact of surface finish on impedance
- High-frequency design considerations
- Via stub management in multilayer designs
- Return path optimization
Material Selection
Substrate Compatibility:
Quality Control and Testing
Incoming Inspection
Visual Examination:
- Surface appearance and uniformity
- Color consistency across the PCB
- Absence of contamination or defects
- Edge quality and coverage
Dimensional Verification:
- Thickness measurement using XRF
- Cross-sectional analysis for layer structure
- Surface roughness measurement
- Adhesion testing protocols
Process Monitoring
In-Process Controls:
- Solution analysis and maintenance
- Temperature and pH monitoring
- Loading calculations and control
- Filtration and contamination management
Statistical Process Control:
- Thickness trend analysis
- Defect rate monitoring
- Customer feedback tracking
- Continuous improvement initiatives
Final Testing
Solderability Testing:
- Wetting balance testing
- Solder spread testing
- Aging studies for shelf life verification
- Multiple reflow testing
Reliability Assessment:
- Thermal cycling testing
- Humidity resistance testing
- Salt spray testing for corrosion resistance
- Mechanical shock and vibration testing
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Black Pad Defect
Symptoms:
- Dark or black appearance at solder joints
- Poor solder joint strength
- Intermittent electrical connections
- Joint failure during testing
Causes:
- Excessive nickel corrosion
- Contaminated chemistry
- Improper solution maintenance
- Incorrect process parameters
Prevention:
- Regular solution analysis and maintenance
- Proper pre-cleaning procedures
- Optimized process parameters
- Quality chemical suppliers
Thickness Variations
Common Problems:
- Uneven gold thickness across the PCB
- Insufficient coverage in certain areas
- Over-plating leading to increased costs
- Under-plating causing reliability issues
Solutions:
- Improved rack design and loading
- Better solution circulation
- Regular equipment maintenance
- Enhanced process monitoring
Contamination Issues
Sources of Contamination:
- Improper cleaning procedures
- Carry-over from previous process steps
- Environmental contamination
- Chemical impurities
Prevention Strategies:
- Comprehensive cleaning protocols
- Controlled environment maintenance
- High-purity chemical usage
- Regular equipment cleaning schedules
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Initial Investment
Equipment Costs:
- Process tanks and heating systems
- Filtration and circulation equipment
- Chemical analysis instrumentation
- Waste treatment systems
Operating Expenses:
- Chemical consumption costs
- Energy usage for heating and circulation
- Labor costs for process management
- Waste treatment and disposal fees
Cost Optimization Strategies
Process Efficiency:
- Optimized loading patterns
- Reduced processing times
- Chemical recycling programs
- Energy-efficient equipment design
Quality Improvements:
- Reduced rework and scrap rates
- Improved first-pass yields
- Extended solution life
- Preventive maintenance programs
Environmental Considerations
Waste Management
Chemical Waste Streams:
- Spent electroless nickel solutions
- Used immersion gold baths
- Rinse water treatment requirements
- Sludge disposal considerations
Environmental Compliance:
- EPA regulations for metal finishing
- Local discharge requirements
- Air emission controls
- Waste minimization strategies
Sustainability Initiatives
Resource Conservation:
- Water recycling systems
- Chemical recovery programs
- Energy efficiency improvements
- Packaging reduction efforts
Green Alternatives:
- Reduced environmental impact chemistries
- Renewable energy usage
- Sustainable supply chain practices
- Life cycle assessment considerations
Future Trends and Innovations
Technology Developments
Process Improvements:
- Advanced chemical formulations
- Improved process control systems
- Automated quality monitoring
- Predictive maintenance technologies
New Applications:
- 5G communication systems
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- Autonomous vehicle electronics
- Renewable energy systems
Market Evolution
Industry Demands:
- Increased miniaturization requirements
- Higher reliability expectations
- Cost reduction pressures
- Environmental compliance needs
Emerging Technologies:
- Additive manufacturing integration
- Advanced packaging applications
- Flexible and stretchable electronics
- Biocompatible electronic devices
Conclusion
ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) represents a mature and versatile surface finishing technology that continues to play a crucial role in modern PCB manufacturing. Its combination of excellent solderability, superior corrosion resistance, and reliable performance makes it the preferred choice for demanding electronic applications across multiple industries.
While ENIG does present certain challenges, including higher costs and potential process complexities, the benefits far outweigh the disadvantages for applications requiring high reliability and long-term performance. The key to successful ENIG implementation lies in understanding the process fundamentals, maintaining proper quality control, and working with experienced suppliers who can provide consistent, high-quality results.
As the electronics industry continues to evolve toward smaller, more complex, and higher-performance devices, ENIG technology will likely remain a cornerstone of advanced PCB manufacturing. Ongoing developments in process chemistry, equipment design, and quality control methods will further enhance its capabilities and expand its applications.
For engineers and manufacturers considering ENIG for their PCB applications, careful evaluation of requirements, costs, and benefits will ensure optimal results. The investment in ENIG technology often pays dividends through improved product reliability, reduced field failures, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
The future of ENIG looks promising, with continued innovations addressing current limitations while expanding into new application areas. As environmental regulations become more stringent and sustainability concerns grow, the industry will likely see developments in more environmentally friendly chemistries and processes that maintain the excellent performance characteristics that make ENIG such a valuable surface finishing option.
Understanding ENIG PCB technology is essential for anyone involved in modern electronics design and manufacturing. This comprehensive guide provides the foundation for making informed decisions about surface finish selection and implementation, ensuring successful outcomes in today’s competitive electronics marketplace.